Broadcast场景
在某些场景下,可能会存在两个输入shape不相同的情况。由于Add接口只支持对shape相同的输入进行计算,因此需要先对输入进行shape变换,再进行Add计算。本节将对满足Broadcast条件的输入在算子实现中的Broadcast处理进行介绍,其他场景可以参考本章节中提供的思路。

Broadcast机制通过扩展较小维度的数据,使得不同shape的输入能够进行运算,从而避免了显式的复制操作,提高了计算效率。数据进行Broadcast需满足:两个输入的维度个数相同,并且仅在某一个维度上的长度不同,某一个输入在此维度的长度为1。比如:shape为(32, 8) 和 (32, 1) 的两个输入可以进行Broadcast,因为它们都是二维,且第一个维度大小相等,而不相等的维度中第二个输入的维度为1,满足条件。
本节中将使用Broadcast接口,因此输入需满足该API相关约束。同时,由于硬件限制,该API的输入地址需满足32字节对齐。本节以输入维度为2、第二个轴(axis = 1)需要Broadcast为例进行说明。完整的样例代码请参见输入Broadcast的Add算子样例。
Tiling实现
与输入shape相同的场景相比,在Tiling结构体中增加相应的成员变量,表示是否需要对输入进行Broadcast、需要对哪个维度进行Broadcast、Broadcast的轴需要扩充的倍数。因此新增四个Tiling结构体成员:
- xLen和yLen:表示两个输入的数据长度。
- axis:表示对输入的哪个维度进行Broadcast。
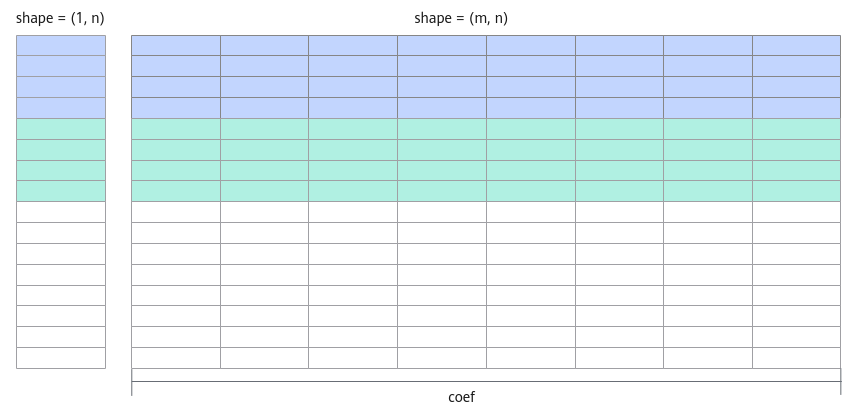
- coef:表示Broadcast的输入需要扩维的倍数。例如,x shape为(m, n), y shape为(1, n), 则coef = m。如下图所示,图中相同颜色部分为单次计算的数据块。
Tiling结构体定义代码如下所示:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
struct AddCustomTilingData { uint32_t xLen; uint32_t yLen; uint32_t coef; uint32_t axis; ... }; |
设需要进行Broadcast的输入长度为shorterAxisLen;不需要进行Broadcast的输入长度为totalLength。
1 2 3 4 |
constexpr uint32_t BLOCK_SIZE = 32; ... // 读入数据 uint32_t totalLength = (xLen > yLen)? xLen : yLen; uint32_t shorterAxisLen = (xLen < yLen)? xLen : yLen; |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 |
constexpr uint32_t BLOCK_SIZE = 32; if (shorterAxisLen % (BLOCK_DIM * BUFFER_NUM) == 0) { uint32_t blockLength = shorterAxisLen / BLOCK_DIM * coef; ... } else { uint32_t formerNum = (shorterAxisLen / BUFFER_NUM) % BLOCK_DIM; uint32_t tailNum = BLOCK_DIM - formerNum; uint32_t formerLength = ((shorterAxisLen / BUFFER_NUM) / BLOCK_DIM + 1) * BUFFER_NUM * coef; uint32_t tailLength = ((shorterAxisLen / BUFFER_NUM) / BLOCK_DIM) * BUFFER_NUM * coef; .... } |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 |
ubBlockAligned = (UB_BLOCK_NUM * alignNum / (coef * BUFFER_NUM) * (coef * BUFFER_NUM) == 0)? UB_BLOCK_NUM : UB_BLOCK_NUM * alignNum / (coef * BUFFER_NUM) * (coef * BUFFER_NUM); ... tileNum = length / ubBlockAligned; if (length % ubBlockAligned == 0 || tileNum == 0) { if (tileNum == 0) { tileNum = 1; } if (length < ubBlockAligned ) { tileLength = length; lastTileLength = tileLength; } else { tileLength = ubBlockAligned; lastTileLength = tileLength; } } else { tileNum = tileNum + 1; tileLength = ubBlockNum; lastTileLength = (length - (tileNum - 1) * tileLength); } |
算子类实现
在核函数初始化阶段,根据Tiling结构体传入的参数确定对哪个输入进行Broadcast。由于针对输入的第二个轴(axis = 1)进行Broadcast,可以计算出,对于需要进行Broadcast的输入,每个核搬入数据长度为blockLength / coef。
初始化函数代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 |
__aicore__ inline void Init(GM_ADDR x, GM_ADDR y, GM_ADDR z, AddCustomTilingData tiling) { GM_ADDR longerInputPtr; GM_ADDR shorterInputPtr; if (tiling.xLen > tiling.yLen) { longerInputPtr = x; shorterInputPtr = y; } else { longerInputPtr = y; shorterInputPtr = x; } this->coef = tiling.coef; if (tiling.isEvenCore) { this->tileNum = tiling.tileNum; this->tileLength = tiling.tileLength / BUFFER_NUM; this->lastTileLength = tiling.lastTileLength; xGm.SetGlobalBuffer((__gm__ dataType *)longerInputPtr + tiling.blockLength * AscendC::GetBlockIdx(), tiling.blockLength); yGm.SetGlobalBuffer((__gm__ dataType *)shorterInputPtr + tiling.blockLength * AscendC::GetBlockIdx() / this->coef, tiling.blockLength / this->coef); zGm.SetGlobalBuffer((__gm__ dataType *)z + tiling.blockLength * AscendC::GetBlockIdx(), tiling.blockLength); } else { if (AscendC::GetBlockIdx() < tiling.formerNum) { this->tileNum = tiling.formerTileNum; this->tileLength = tiling.formerTileLength / BUFFER_NUM; this->lastTileLength = tiling.formerLastTileLength; xGm.SetGlobalBuffer((__gm__ dataType *)longerInputPtr + tiling.formerLength * AscendC::GetBlockIdx(), tiling.formerLength); yGm.SetGlobalBuffer((__gm__ dataType *)shorterInputPtr + tiling.formerLength * AscendC::GetBlockIdx() / this->coef, tiling.formerLength / this->coef); zGm.SetGlobalBuffer((__gm__ dataType *)z + tiling.formerLength * AscendC::GetBlockIdx(), tiling.formerLength); } else { this->tileNum = tiling.tailTileNum; this->tileLength = tiling.tailTileLength / BUFFER_NUM; this->lastTileLength = tiling.tailLastTileLength; xGm.SetGlobalBuffer((__gm__ dataType *)longerInputPtr + tiling.formerLength * tiling.formerNum + tiling.tailLength * (AscendC::GetBlockIdx() - tiling.formerNum), tiling.tailLength); yGm.SetGlobalBuffer((__gm__ dataType *)shorterInputPtr + tiling.formerLength * tiling.formerNum / this->coef + tiling.tailLength * (AscendC::GetBlockIdx() - tiling.formerNum) / this->coef, tiling.tailLength / this->coef); zGm.SetGlobalBuffer((__gm__ dataType *)z + tiling.formerLength * tiling.formerNum + tiling.tailLength * (AscendC::GetBlockIdx() - tiling.formerNum), tiling.tailLength); } } pipe.InitBuffer(inQueueX, BUFFER_NUM, this->tileLength * sizeof(dataType)); pipe.InitBuffer(inQueueY, BUFFER_NUM, this->coef * sizeof(dataType)); pipe.InitBuffer(outQueueZ, BUFFER_NUM, this->tileLength * sizeof(dataType)); pipe.InitBuffer(tmpBuf2, this->tileLength * sizeof(dataType)); } |
由于数据是向coef对齐的,在数据拷贝的过程中可能会出现地址不满足32字节对齐的场景,因此CopyIn函数、CopyOut函数中使用DataCopyPad进行数据拷贝。
CopyIn函数实现代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 |
__aicore__ inline void CopyIn(int32_t progress) { AscendC::LocalTensor<dataType> xLocal = inQueueX.AllocTensor<dataType>(); AscendC::LocalTensor<dataType> yLocal = inQueueY.AllocTensor<dataType>(); AscendC::DataCopyExtParams copyXParams = {1, (uint32_t)(this->tileLength * sizeof(dataType)), 0, 0, 0}; AscendC::DataCopyExtParams copyYParams = {1, (uint32_t)(this->tileLength * sizeof(dataType) / this->coef), 0, 0, 0}; AscendC::DataCopyPadExtParams<dataType> padParams = {false, 0, 0, 0}; if ((progress == (this->tileNum * BUFFER_NUM - 2)) || (progress == (this->tileNum * BUFFER_NUM - 1))) { AscendC::DataCopyPad<dataType>(xLocal, xGm[(progress - LAST_TWO_TILE) * this->tileLength + this->lastTileLength], copyXParams, padParams); AscendC::DataCopyPad<dataType>(yLocal, yGm[((progress - LAST_TWO_TILE) * this->tileLength + this->lastTileLength) / this->coef], copyYParams, padParams); } else { AscendC::DataCopyPad<dataType>(xLocal, xGm[progress * this->tileLength], copyXParams, padParams); AscendC::DataCopyPad<dataType>(yLocal, yGm[progress * this->tileLength / this->coef], copyYParams, padParams); } inQueueX.EnQue(xLocal); inQueueY.EnQue(yLocal); } |
CopyOut函数实现代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
__aicore__ inline void CopyOut(int32_t progress) { AscendC::LocalTensor<dataType> zLocal = outQueueZ.DeQue<dataType>(); AscendC::DataCopyExtParams copyParams = {1, (uint32_t)(this->tileLength * sizeof(dataType)), 0, 0, 0}; if ((progress == (this->tileNum * BUFFER_NUM - 2)) || (progress == (this->tileNum * BUFFER_NUM - 1))) { AscendC::DataCopyPad<dataType>(zGm[(progress - LAST_TWO_TILE) * this->tileLength + this->lastTileLength], zLocal, copyParams); } else { AscendC::DataCopyPad<dataType>(zGm[progress * this->tileLength], zLocal, copyParams); } outQueueZ.FreeTensor(zLocal); } |
在Compute函数中,调用Add接口前需要先对输入进行Broadcast。这里需要计算Broadcast前后的shape。基于前文提到的数据关系,可以计算得出Broadcast前后的shape分别为{tileLength / broadcastCoef, 1}和{tileLength / broadcastCoef, broadcastCoef}。在此基础上对输入进行Broadcast,并将计算结果存入临时空间中,然后进行Add计算。实现代码示例如下所示:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
__aicore__ inline void Compute(int32_t progress) { AscendC::LocalTensor<dataType> xLocal = inQueueX.DeQue<dataType>(); AscendC::LocalTensor<dataType> yLocal = inQueueY.DeQue<dataType>(); AscendC::LocalTensor<dataType> zLocal = outQueueZ.AllocTensor<dataType>(); AscendC::LocalTensor<dataType> broadcastTmpTensor = broadcastTmpBuf.Get<dataType>(); uint32_t dstShape[] = {this->tileLength / this->coef, this->coef}; uint32_t srcShape[] = {this->tileLength / this->coef, 1}; AscendC::BroadCast<dataType, 2, 1>(broadcastTmpTensor, yLocal, dstShape, srcShape); ... } |