LayerNormGrad
函数功能
LayerNormGrad是一个函数,用于计算LayerNorm的反向传播梯度。该接口单独使用会输出x、resForGamma;也可以和LayerNormGradBeta配合使用,输出的resForGamma传递给LayerNormGradBeta, LayerNormGradBeta接口会输出gamma和beta,配合使用时就可以同时得到x、Gamma、beta。
算法公式为:
pd_xl(BSH) = data_dy * data_gamma pd_var(H) = np.sum(((-0.5) * pd_xl * (data_x - data_mean) * np.power((data_variance + EPSLON), (-1.5))), reduce_axis, keepdims=True) pd_mean(BS1) = np.sum(((-1.0) * pd_xl * np.power((data_variance + EPSLON), (-0.5))), reduce_axis, keepdims=True) + pd_var * (1.0 / H) * np.sum(((-2.0) * (data_x - data_mean)), reduce_axis, keepdims=True) pd_x(BSH) = pd_xl * np.power((data_variance + EPSLON), (-0.5)) + pd_var * (2.0 / H) * (data_x - data_mean) + pd_mean * (1.0 / H) res_for_gamma(BSH) = (data_x - data_mean) * np.power((data_variance + EPSLON), (-0.5))
实现原理
以float类型,ND格式,输入为inputDy[B, S, H], inputX[B, S, H], inputVariance[B, S], inputMean[B, S], inputGamma[H]为例,描述LayerNormGrad高阶API内部算法框图,如下图所示。
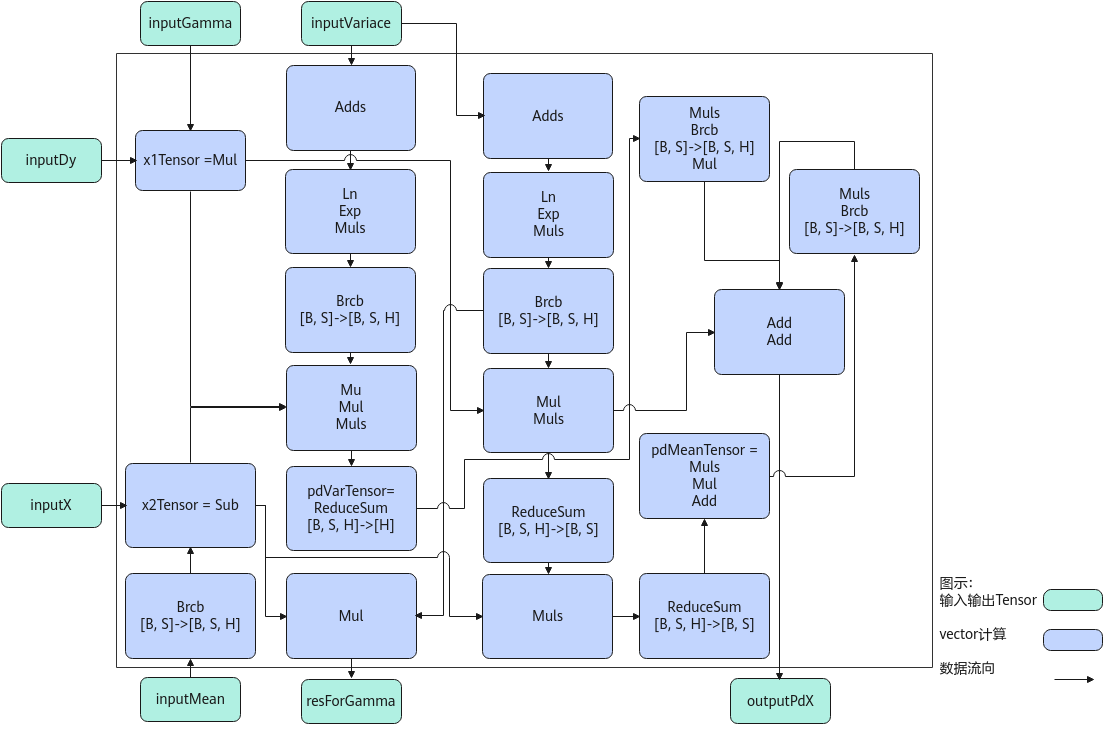
计算过程分为如下几步,均在Vector上进行:
- ComputePdX1步骤:计算inputDy*inputGamma,结果存储至x1Tensor;
- ComputePdX2步骤:inputMean先通过Brcb将shape扩充到[B, S, H],再计算inputX-inputMean,结果存储至x2Tensor;
- ComputePdVar步骤:实现公式np.sum(((-0.5) * x1Tensor * x2Tensor * np.power((inputVariace + EPSLON), (-1.5))))的计算,power方法的实现通过Ln、Exp、Muls三条基础API组合实现,结果存储至pdVarTensor;
- ComputePdMean:实现公式np.sum(((-1.0) * x1Tensor * np.power((inputVariace + EPSLON), (-0.5)))) + pd_var * (1.0 / H) * np.sum(((-2.0) * (x2Tensor)))的计算,power方法通过Ln、Exp、Muls三条基础API组合实现,结果存储至pdMeanTensor。同时,利用中间计算结果,根据公式x2Tensor * np.power((inputVariace + EPSLON), (-1.5)),计算出resForGamma的结果;
- ComputePdX步骤:实现公式x1Tensor * np.power((inputVariace + EPSLON), (-0.5)) + pd_var*(2.0 / H)*(x2Tensor) + pd_mean*(1.0 / H)的计算,结果存入outputPdX。
函数原型
由于该接口的内部实现中涉及复杂的计算,需要额外的临时空间来存储计算过程中的中间变量。临时空间大小BufferSize的获取方法:通过LayerNormGrad Tiling中提供的GetLayerNormGradMaxMinTmpSize接口获取所需最大和最小临时空间大小,最小空间可以保证功能正确,最大空间用于提升性能。
临时空间支持接口框架申请和开发者通过sharedTmpBuffer入参传入两种方式,因此LayerNormGrad接口的函数原型有两种:
- 通过sharedTmpBuffer入参传入临时空间
1 2
template <typename T, bool isReuseSource = false> __aicore__ inline void LayerNormGrad(const LocalTensor<T> &outputPdX, const LocalTensor<T> &resForGamma, const LocalTensor<T> &inputDy, const LocalTensor<T> &inputX, const LocalTensor<T> &inputVariance, const LocalTensor<T> &inputMean, const LocalTensor<T> &inputGamma, LocalTensor<uint8_t> &sharedTmpBuffer, T epsilon, LayerNormGradTiling &tiling)
该方式下开发者需自行申请并管理临时内存空间并管理,并在接口调用完成后,复用该部分内存,内存不会反复申请释放,灵活性较高,内存利用率也较高。
- 接口框架申请临时空间
1 2
template <typename T, bool isReuseSource = false> __aicore__ inline void LayerNormGrad(const LocalTensor<T> &outputPdX, const LocalTensor<T> &resForGamma, const LocalTensor<T> &inputDy, const LocalTensor<T> &inputX, const LocalTensor<T> &inputVariance, const LocalTensor<T> &inputMean, const LocalTensor<T> &inputGamma, T epsilon, LayerNormGradTiling &tiling)
该方式下开发者无需申请,但是需要预留临时空间的大小。
参数说明
|
参数名 |
描述 |
|---|---|
|
T |
操作数的数据类型。 |
|
isReuseSource |
是否允许修改源操作数,默认值为false。如果开发者允许源操作数被改写,可以使能该参数,使能后能够节省部分内存空间。 设置为true,则本接口内部计算时复用inputX的内存空间,节省内存空间;设置为false,则本接口内部计算时不复用inputX的内存空间。 对于float数据类型输入支持开启该参数,half数据类型输入不支持开启该参数。 isReuseSource的使用样例请参考更多样例。 |
|
参数名称 |
输入/输出 |
含义 |
|---|---|---|
|
outputPdX |
输出 |
目的操作数,类型为LocalTensor,shape为[B, S, H],LocalTensor数据结构的定义请参考LocalTensor。尾轴长度需要32B对齐。 Atlas A2训练系列产品/Atlas 800I A2推理产品,支持的数据类型为:half/float Atlas推理系列产品AI Core,支持的数据类型为:half/float |
|
resForGamma |
输出 |
目的操作数,类型为LocalTensor,shape为[B, S, H],LocalTensor数据结构的定义请参考LocalTensor。尾轴长度需要32B对齐。 Atlas A2训练系列产品/Atlas 800I A2推理产品,支持的数据类型为:half/float Atlas推理系列产品AI Core,支持的数据类型为:half/float |
|
inputDy |
输入 |
源操作数,类型为LocalTensor,shape为[B, S, H],LocalTensor数据结构的定义请参考LocalTensor。inputDy的数据类型需要与目的操作数保持一致,尾轴长度需要32B对齐。 Atlas A2训练系列产品/Atlas 800I A2推理产品,支持的数据类型为:half/float Atlas推理系列产品AI Core,支持的数据类型为:half/float |
|
inputX |
输入 |
源操作数,类型为LocalTensor,shape为[B, S, H],LocalTensor数据结构的定义请参考LocalTensor。inputX的数据类型需要与目的操作数保持一致,尾轴长度需要32B对齐。 Atlas A2训练系列产品/Atlas 800I A2推理产品,支持的数据类型为:half/float Atlas推理系列产品AI Core,支持的数据类型为:half/float |
|
inputVariance |
输入 |
方差,类型为LocalTensor,shape为[B, S],LocalTensor数据结构的定义请参考LocalTensor。inputVariance的数据类型需要与目的操作数保持一致,尾轴长度需要32B对齐。需提前调用LayerNorm接口获取方差。 Atlas A2训练系列产品/Atlas 800I A2推理产品,支持的数据类型为:half/float Atlas推理系列产品AI Core,支持的数据类型为:half/float |
|
inputMean |
输入 |
均值,类型为LocalTensor,shape为[B, S],LocalTensor数据结构的定义请参考LocalTensor。inputMean的数据类型需要与目的操作数保持一致,尾轴长度需要32B对齐。需提前调用LayerNorm接口获取均值。 Atlas A2训练系列产品/Atlas 800I A2推理产品,支持的数据类型为:half/float Atlas推理系列产品AI Core,支持的数据类型为:half/float |
|
inputGamma |
输入 |
源操作数,类型为LocalTensor,shape为[H],LocalTensor数据结构的定义请参考LocalTensor。inputGamma的数据类型需要与目的操作数保持一致,尾轴长度需要32B对齐。 Atlas A2训练系列产品/Atlas 800I A2推理产品,支持的数据类型为:half/float Atlas推理系列产品AI Core,支持的数据类型为:half/float |
|
sharedTmpBuffer |
输入 |
共享缓冲区,用于存放API内部计算产生的临时数据。该方式开发者可以自行管理sharedTmpBuffer内存空间,并在接口调用完成后,复用该部分内存,内存不会反复申请释放,灵活性较高,内存利用率也较高。 类型为LocalTensor,支持的TPosition为VECIN/VECCALC/VECOUT。 Atlas A2训练系列产品/Atlas 800I A2推理产品,支持的数据类型为:half/float Atlas推理系列产品AI Core,支持的数据类型为:half/float |
|
epsilon |
输入 |
防除零的权重系数。 |
|
tiling |
输入 |
LayerNormGrad计算所需Tiling信息。 |
返回值
无
支持的型号
Atlas A2训练系列产品/Atlas 800I A2推理产品
Atlas推理系列产品AI Core
约束说明
- 操作数地址偏移对齐要求请参见通用约束。
- src和dst的Tensor空间可以复用。
- 仅支持输入shape为ND格式。
- 输入数据不满足对齐要求时,开发者需要进行补齐,补齐的数据应设置为0,防止出现异常值从而影响网络计算。
- 不支持对尾轴H轴的切分。
调用示例
本样例中,输入inputX和inputDy的shape为[2, 32, 16],inputVariance和inputMean的shape为[2, 32],inputGamma的shape为[16]。输出outputPdX和resForGamma的shape为[2, 32, 16]。数据排布均为ND格式,数据类型均为float,不复用源操作数的内存空间。
#include "kernel_operator.h"
namespace MyCustomKernel {
struct VecTiling {
LayerNormGradTiling layernormGradTilingData;
float epsilon = 0;
};
template <bool isReuseSource = false> class KernelLayernormGrad {
public:
__aicore__ inline KernelLayernormGrad() {}
__aicore__ inline void Init(GM_ADDR inputXGm, GM_ADDR inputDyGm, GM_ADDR inputVarianceGm, GM_ADDR inputMeanGm,
GM_ADDR inputGammaGm, GM_ADDR outputPdXGm, GM_ADDR resForGammaGm, VecTiling tilingData)
{
this->epsilon = tilingData.epsilon;
tiling_ = tilingData.layernormGradTilingData;
this->bLength = tiling_.bLength;
this->sLength = tiling_.sLength;
this->hLength = tiling_.hLength;
bshLength = bLength * sLength * hLength;
bsLength = bLength * sLength;
inputXGlobal.SetGlobalBuffer(reinterpret_cast<__gm__ float *>(inputXGm), bshLength);
inputDyGlobal.SetGlobalBuffer(reinterpret_cast<__gm__ float *>(inputDyGm), bshLength);
inputVarianceGlobal.SetGlobalBuffer(reinterpret_cast<__gm__ float *>(inputVarianceGm), bsLength);
inputMeanGlobal.SetGlobalBuffer(reinterpret_cast<__gm__ float *>(inputMeanGm), bsLength);
inputGammaGlobal.SetGlobalBuffer(reinterpret_cast<__gm__ float *>(inputGammaGm), hLength);
outputPdXGlobal.SetGlobalBuffer(reinterpret_cast<__gm__ float *>(outputPdXGm), bshLength);
outputResForGammaGlobal.SetGlobalBuffer(reinterpret_cast<__gm__ float *>(resForGammaGm), bshLength);
pipe.InitBuffer(inQueueX, 1, sizeof(float) * bshLength);
pipe.InitBuffer(inQueueDy, 1, sizeof(float) * bshLength);
pipe.InitBuffer(inQueueVariance, 1, sizeof(float) * bsLength);
pipe.InitBuffer(inQueueMean, 1, sizeof(float) * bsLength);
pipe.InitBuffer(inQueueGamma, 1, sizeof(float) * hLength);
pipe.InitBuffer(outQueuePdX, 1, sizeof(float) * bshLength);
pipe.InitBuffer(outQueueResForGamma, 1, sizeof(float) * bshLength);
}
__aicore__ inline void Process()
{
CopyIn();
Compute();
CopyOut();
}
private:
__aicore__ inline void CopyIn()
{
AscendC::LocalTensor<float> inputXLocal = inQueueX.AllocTensor<float>();
AscendC::LocalTensor<float> inputDyLocal = inQueueDy.AllocTensor<float>();
AscendC::LocalTensor<float> inputVarianceLocal = inQueueVariance.AllocTensor<float>();
AscendC::LocalTensor<float> inputMeanLocal = inQueueMean.AllocTensor<float>();
AscendC::LocalTensor<float> inputGammaLocal = inQueueGamma.AllocTensor<float>();
AscendC::DataCopy(inputXLocal, inputXGlobal, bshLength);
AscendC::DataCopy(inputDyLocal, inputDyGlobal, bshLength);
AscendC::DataCopy(inputVarianceLocal, inputVarianceGlobal, bsLength);
AscendC::DataCopy(inputMeanLocal, inputMeanGlobal, bsLength);
AscendC::DataCopy(inputGammaLocal, inputGammaGlobal, hLength);
inQueueX.EnQue(inputXLocal);
inQueueDy.EnQue(inputDyLocal);
inQueueVariance.EnQue(inputVarianceLocal);
inQueueMean.EnQue(inputMeanLocal);
inQueueGamma.EnQue(inputGammaLocal);
}
__aicore__ inline void Compute()
{
AscendC::LocalTensor<float> inputXLocal = inQueueX.DeQue<float>();
AscendC::LocalTensor<float> inputDyLocal = inQueueDy.DeQue<float>();
AscendC::LocalTensor<float> inputVarianceLocal = inQueueVariance.DeQue<float>();
AscendC::LocalTensor<float> inputMeanLocal = inQueueMean.DeQue<float>();
AscendC::LocalTensor<float> inputGammaLocal = inQueueGamma.DeQue<float>();
AscendC::LocalTensor<float> outputPdXLocal = outQueuePdX.AllocTensor<float>();
AscendC::LocalTensor<float> outputResForGammaLocal = outQueueResForGamma.AllocTensor<float>();
AscendC::LayerNormGrad<float, isReuseSource>(outputPdXLocal, outputResForGammaLocal,
inputDyLocal, inputXLocal, inputVarianceLocal, inputMeanLocal, inputGammaLocal,
(float)epsilon, tiling_);
outQueuePdX.EnQue(outputPdXLocal);
outQueueResForGamma.EnQue(outputResForGammaLocal);
inQueueX.FreeTensor(inputXLocal);
inQueueDy.FreeTensor(inputDyLocal);
inQueueVariance.FreeTensor(inputVarianceLocal);
inQueueMean.FreeTensor(inputMeanLocal);
inQueueGamma.FreeTensor(inputGammaLocal);
}
__aicore__ inline void CopyOut()
{
AscendC::LocalTensor<float> outputPdXLocal = outQueuePdX.DeQue<float>();
AscendC::LocalTensor<float> outputResForGammaLocal = outQueueResForGamma.DeQue<float>();
AscendC::DataCopy(outputPdXGlobal, outputPdXLocal, bshLength);
AscendC::DataCopy(outputResForGammaGlobal, outputResForGammaLocal, bshLength);
outQueuePdX.FreeTensor(outputPdXLocal);
outQueueResForGamma.FreeTensor(outputResForGammaLocal);
}
private:
AscendC::GlobalTensor<float> inputXGlobal;
AscendC::GlobalTensor<float> inputDyGlobal;
AscendC::GlobalTensor<float> inputVarianceGlobal;
AscendC::GlobalTensor<float> inputMeanGlobal;
AscendC::GlobalTensor<float> inputGammaGlobal;
AscendC::GlobalTensor<float> outputPdXGlobal;
AscendC::GlobalTensor<float> outputResForGammaGlobal;
AscendC::TPipe pipe;
AscendC::TQue<AscendC::QuePosition::VECIN, 1> inQueueX;
AscendC::TQue<AscendC::QuePosition::VECIN, 1> inQueueDy;
AscendC::TQue<AscendC::QuePosition::VECIN, 1> inQueueVariance;
AscendC::TQue<AscendC::QuePosition::VECIN, 1> inQueueMean;
AscendC::TQue<AscendC::QuePosition::VECIN, 1> inQueueGamma;
AscendC::TQue<AscendC::QuePosition::VECOUT, 1> outQueuePdX;
AscendC::TQue<AscendC::QuePosition::VECOUT, 1> outQueueResForGamma;
uint32_t bLength;
uint32_t sLength;
uint32_t hLength;
float epsilon;
LayerNormGradTiling tiling_;
uint32_t bshLength;
uint32_t bsLength;
};
}
extern "C" __global__ __aicore__ void layernorm_grad_custom(GM_ADDR inputXGm, GM_ADDR inputDyGm, GM_ADDR inputVarianceGm,
GM_ADDR inputMeanGm, GM_ADDR inputGammaGm, GM_ADDR outputPdXGm, GM_ADDR resForGammaGm,
GM_ADDR workspace, GM_ADDR tiling)
{
if ASCEND_IS_AIC {
return;
}
MyCustomKernel::VecTiling tilingData;
CopyTiling(&tilingData, tiling);
MyCustomKernel::KernelLayernormGrad<false> op;
op.Init(inputXGm, inputDyGm, inputVarianceGm, inputMeanGm, inputGammaGm, outputPdXGm, resForGammaGm, tilingData);
op.Process();
}