aclnnBatchNormGatherStatsWithCounts
接口原型
每个算子有两段接口,必须先调用“aclnnXxxGetWorkspaceSize”接口获取入参并根据计算流程计算所需workspace大小,再调用“aclnnXxx”接口执行计算。两段式接口如下:
- 第一段接口:aclnnStatus aclnnBatchNormGatherStatsWithCountsGetWorkspaceSize(const aclTensor* input, const aclTensor* mean, const aclTensor* invstd, aclTensor* runningMean, aclTensor* runningVar, double momentum, double eps, const aclTensor* counts, aclTensor* meanAllOut, aclTensor* invstdAllOut, uint64_t* workspaceSize, aclOpExecutor** executor)
- 第二段接口:aclnnStatus aclnnBatchNormGatherStatsWithCounts(void* workspace, uint64_t workspaceSize, aclOpExecutor* executor, const aclrtStream stream)
功能描述
- 算子功能:多卡BatchNorm场景下实现SyncBatchNorm,需通过aclnnBatchNormStats、aclnnBatchNormGatherStatsWithCounts和aclnnBatchNormElemt算子组合实现。其中aclnnBatchNormGatherStatsWithCounts主要收集所有device的均值和方差,并更新全局的均值和方差,计算时依赖aclnnBatchNormStats计算单卡数据的均值和标准差的倒数。
BatchNorm的性能和BatchSize相关,BatchSize越大,BatchNorm的统计量也会越准。对于目标检测类似的任务,占用显存较高,一张显卡往往只能使用较少的图片(比如2张)来训练,这就导致BN的表现变差。为解决该问题,需要实现SyncBatchNorm,即所有卡共享同一个BN,得到全局的统计量。
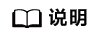
- 计算公式:
runningMean(M)与runningVar(V)更新公式如下:
aclnnBatchNormGatherStatsWithCountsGetWorkspaceSize
- 接口定义:
aclnnStatus aclnnBatchNormGatherStatsWithCountsGetWorkspaceSize(const aclTensor* input, const aclTensor* mean, const aclTensor* invstd, aclTensor* runningMean, aclTensor* runningVar, double momentum, double eps, const aclTensor* counts, aclTensor* meanAllOut, aclTensor* invstdAllOut, uint64_t* workspaceSize, aclOpExecutor** executor)
- 参数说明:
- input:Device侧的aclTensor,输入Tensor,数据类型支持FLOAT16、FLOAT,支持非连续Tensor,数据格式五维及以下支持NCDHW、NCHW、NCL、NC,六维到八维支持ND。
- mean:输入数据均值,Device侧的aclTensor,数据类型支持FLOAT16、FLOAT,支持非连续的Tensor,数据格式为ND。二维Tensor,第一轴对应的大小与input入参中的C轴长度相同。
- invstd:输入数据标准差的倒数,Device侧的aclTensor,数据类型仅支持FLOAT16、FLOAT,支持非连续的Tensor,数据格式为ND。二维Tensor,第一轴对应的大小与input入参中的C轴长度相同。
- runningMean:训练时数据的均值,Device侧的aclTensor,数据类型仅支持FLOAT,支持非连续的Tensor,数据格式为ND。一维Tensor,长度与input入参中的C轴长度相同。
- runningVar:训练时数据的方差,Device侧的aclTensor,数据类型仅支持FLOAT,支持非连续的Tensor,数据格式为ND。一维Tensor,长度与input入参中的C轴长度相同。
- momentum:runningMean和runningVar的指数平滑参数,默认0.1。
- eps:用于防止做BN时,分母出现0的情况,默认值为1e-5。
- counts:输入数据的元素个数,Device侧的aclTensor,数据类型仅支持FLOAT,支持非连续的Tensor,数据格式为ND。一维Tensor,长度与mean或invstd入参0轴的长度相同。
- meanAll:SyncBatchNorm后,所有卡上数据的均值,Device侧的aclTensor,数据类型仅支持FLOAT16、FLOAT,支持非连续的Tensor,数据格式为ND。
- invstdAll:SyncBatchNorm后,所有卡上数据的标准差的倒数,Device侧的aclTensor,数据类型仅支持FLOAT16、FLOAT,支持非连续的Tensor,数据格式为ND。
- workspaceSize:返回用户需要在Device侧申请的workspace大小。
- executor:返回op执行器,包含了算子计算流程。
- 返回值:
返回aclnnStatus状态码,具体参见aclnn返回码。

第一段接口完成入参校验,出现以下场景时报错:
- 返回161001(ACLNN_ERR_PARAM_NULLPTR):传入的指针类型入参是空指针。
- 返回161002(ACLNN_ERR_PARAM_INVALID):
- input、mean、invstd、runningMean、runningVar、counts数据类型和数据格式不在支持的范围内。
- input、mean、invstd、runningMean、runningVar、counts的shape不在支持的范围内。
aclnnBatchNormGatherStatsWithCounts
- 接口定义:
- aclnnStatus aclnnBatchNormGatherStatsWithCounts(void* workspace, uint64_t workspaceSize, aclOpExecutor* executor, const aclrtStream stream)
- 参数说明:
- workspace:在Device侧申请的workspace内存起址。
- workspaceSize:在Device侧申请的workspace大小,由第一段接口aclnnBatchNormGatherStatsWithCountsGetWorkspaceSize获取。
- executor:op执行器,包含了算子计算流程。
- stream:指定执行任务的AscendCL stream流。
- 返回值:
返回aclnnStatus状态码,具体参见aclnn返回码。
调用示例
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 | #include <iostream> #include <vector> #include "acl/acl.h" #include "aclnnop/aclnn_batch_norm_gather_stats_with_counts.h" #define CHECK_RET(cond, return_expr) \ do { \ if (!(cond)) { \ return_expr; \ } \ } while (0) #define LOG_PRINT(message, ...) \ do { \ printf(message, ##__VA_ARGS__); \ } while (0) int64_t GetShapeSize(const std::vector<int64_t>& shape) { int64_t shape_size = 1; for (auto i : shape) { shape_size *= i; } return shape_size; } int Init(int32_t deviceId, aclrtContext* context, aclrtStream* stream) { // 固定写法,AscendCL初始化 auto ret = aclInit(nullptr); CHECK_RET(ret == ACL_SUCCESS, LOG_PRINT("aclInit failed. ERROR: %d\n", ret); return ret); ret = aclrtSetDevice(deviceId); CHECK_RET(ret == ACL_SUCCESS, LOG_PRINT("aclrtSetDevice failed. ERROR: %d\n", ret); return ret); ret = aclrtCreateContext(context, deviceId); CHECK_RET(ret == ACL_SUCCESS, LOG_PRINT("aclrtCreateContext failed. ERROR: %d\n", ret); return ret); ret = aclrtSetCurrentContext(*context); CHECK_RET(ret == ACL_SUCCESS, LOG_PRINT("aclrtSetCurrentContext failed. ERROR: %d\n", ret); return ret); ret = aclrtCreateStream(stream); CHECK_RET(ret == ACL_SUCCESS, LOG_PRINT("aclrtCreateStream failed. ERROR: %d\n", ret); return ret); return 0; } template <typename T> int CreateAclTensor(const std::vector<T>& hostData, const std::vector<int64_t>& shape, void** deviceAddr, aclDataType dataType, aclTensor** tensor) { auto size = GetShapeSize(shape) * sizeof(T); // 调用aclrtMalloc申请device侧内存 auto ret = aclrtMalloc(deviceAddr, size, ACL_MEM_MALLOC_HUGE_FIRST); CHECK_RET(ret == ACL_SUCCESS, LOG_PRINT("aclrtMalloc failed. ERROR: %d\n", ret); return ret); // 调用aclrtMemcpy将Host侧数据拷贝到device侧内存上 ret = aclrtMemcpy(*deviceAddr, size, hostData.data(), size, ACL_MEMCPY_HOST_TO_DEVICE); CHECK_RET(ret == ACL_SUCCESS, LOG_PRINT("aclrtMemcpy failed. ERROR: %d\n", ret); return ret); // 计算连续tensor的strides std::vector<int64_t> strides(shape.size(), 1); for (int64_t i = shape.size() - 2; i >= 0; i--) { strides[i] = shape[i + 1] * strides[i + 1]; } // 调用aclCreateTensor接口创建aclTensor *tensor = aclCreateTensor(shape.data(), shape.size(), dataType, strides.data(), 0, aclFormat::ACL_FORMAT_ND, shape.data(), shape.size(), *deviceAddr); return 0; } int main() { // 1. (固定写法)device/context/stream初始化, 参考AscendCL对外接口列表 // 根据自己的实际device填写deviceId int32_t deviceId = 0; aclrtContext context; aclrtStream stream; auto ret = Init(deviceId, &context, &stream); // check根据自己的需要处理 CHECK_RET(ret == 0, LOG_PRINT("Init acl failed. ERROR: %d\n", ret); return ret); // 2. 构造输入与输出,需要根据API的接口自定义构造 std::vector<int64_t> inputShape = {2, 4, 2}; std::vector<int64_t> meanShape = {2, 4}; std::vector<int64_t> invstdShape = {2, 4}; std::vector<int64_t> countShape = {2}; std::vector<int64_t> meanOutShape = {4}; std::vector<int64_t> invstdOutShape = {4}; double eps = 1e-2; void* inputDeviceAddr = nullptr; void* meanDeviceAddr = nullptr; void* invstdDeviceAddr = nullptr; void* countDeviceAddr = nullptr; void* meanOutDeviceAddr = nullptr; void* invstdOutDeviceAddr = nullptr; aclTensor* input = nullptr; aclTensor* mean = nullptr; aclTensor* invstd = nullptr; aclTensor* count = nullptr; aclTensor* meanOut = nullptr; aclTensor* invstdOut = nullptr; std::vector<float> inputHostData = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15}; std::vector<float> meanHostData = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8}; std::vector<float> invstdHostData = {5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12}; std::vector<float> countHostData = {1, 2}; std::vector<float> meanOutHostData = {0, 0, 0, 0}; std::vector<float> invstdOutHostData = {0, 0, 0, 0}; // 创建input aclTensor ret = CreateAclTensor(inputHostData, inputShape, &inputDeviceAddr, aclDataType::ACL_FLOAT, &input); CHECK_RET(ret == ACL_SUCCESS, return ret); // 创建mean aclTensor ret = CreateAclTensor(meanHostData, meanShape, &meanDeviceAddr, aclDataType::ACL_FLOAT, &mean); CHECK_RET(ret == ACL_SUCCESS, return ret); // 创建invstd aclTensor ret = CreateAclTensor(invstdHostData, invstdShape, &invstdDeviceAddr, aclDataType::ACL_FLOAT, &invstd); CHECK_RET(ret == ACL_SUCCESS, return ret); // 创建invstd aclTensor ret = CreateAclTensor(countHostData, countShape, &countDeviceAddr, aclDataType::ACL_FLOAT, &count); CHECK_RET(ret == ACL_SUCCESS, return ret); // 创建meanOut aclTensor ret = CreateAclTensor(meanOutHostData, meanOutShape, &meanOutDeviceAddr, aclDataType::ACL_FLOAT, &meanOut); CHECK_RET(ret == ACL_SUCCESS, return ret); // 创建invstdOut aclTensor ret = CreateAclTensor(invstdOutHostData, invstdOutShape, &invstdOutDeviceAddr, aclDataType::ACL_FLOAT, &invstdOut); CHECK_RET(ret == ACL_SUCCESS, return ret); // 3.调用CANN算子库API,需要修改为具体的算子接口 uint64_t workspaceSize = 0; aclOpExecutor* executor; // 调用aclnnBatchNormGatherStatsWithCounts第一段接口 ret = aclnnBatchNormGatherStatsWithCountsGetWorkspaceSize(input, mean, invstd, nullptr, nullptr, 1e-4, 1e-2, count, meanOut, invstdOut, &workspaceSize, &executor); CHECK_RET(ret == ACL_SUCCESS, LOG_PRINT("aclnnBatchNormGatherStatsWithCountsGetWorkspaceSize failed. ERROR: %d\n", ret); return ret); // 根据第一段接口计算出的workspaceSize申请device内存 void* workspaceAddr = nullptr; if (workspaceSize > 0) { ret = aclrtMalloc(&workspaceAddr, workspaceSize, ACL_MEM_MALLOC_HUGE_FIRST); CHECK_RET(ret == ACL_SUCCESS, LOG_PRINT("allocate workspace failed. ERROR: %d\n", ret); return ret;); } // 调用aclnnBatchNormGatherStatsWithCounts第二段接口 ret = aclnnBatchNormGatherStatsWithCounts(workspaceAddr, workspaceSize, executor, stream); CHECK_RET(ret == ACL_SUCCESS, LOG_PRINT("aclnnBatchNormGatherStatsWithCounts failed. ERROR: %d\n", ret); return ret); // 4. (固定写法)同步等待任务执行结束 ret = aclrtSynchronizeStream(stream); CHECK_RET(ret == ACL_SUCCESS, LOG_PRINT("aclrtSynchronizeStream failed. ERROR: %d\n", ret); return ret); // 5. 获取输出的值,将device侧内存上的结果拷贝至Host侧,需要根据具体API的接口定义修改 auto size = GetShapeSize(meanOutShape); std::vector<float> resultData(size, 0); ret = aclrtMemcpy(resultData.data(), resultData.size() * sizeof(resultData[0]), meanOutDeviceAddr, size * sizeof(float), ACL_MEMCPY_DEVICE_TO_HOST); CHECK_RET(ret == ACL_SUCCESS, LOG_PRINT("copy result from device to host failed. ERROR: %d\n", ret); return ret); for (int64_t i = 0; i < size; i++) { LOG_PRINT("result[%ld] is: %f\n", i, resultData[i]); } // 6. 释放aclTensor和aclScalar,需要根据具体API的接口定义修改 aclDestroyTensor(input); aclDestroyTensor(mean); aclDestroyTensor(invstd); aclDestroyTensor(count); aclDestroyTensor(meanOut); aclDestroyTensor(invstdOut); return 0; } |
父主题: NN类算子接口