Gelu
功能说明
在神经网络中,GELU是一个重要的激活函数,其灵感来源于Relu和Dropout,在激活中引入了随机正则的思想。计算公式如下,其中PAR表示矢量计算单元一个迭代能够处理的元素个数 :
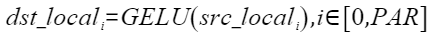
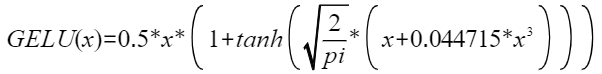 ,化简后可得
,化简后可得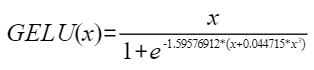
函数原型
1 2 | template <typename T, bool highPrecision = false, bool highPerformance = false> __aicore__ inline void Gelu(const LocalTensor<T>& dstLocal, const LocalTensor<T>& srcLocal, const uint32_t dataSize) |
1 2 | template <typename T, bool highPrecision = false, bool highPerformance = false> __aicore__ inline void Gelu(const LocalTensor<T>& dstLocal, const LocalTensor<T>& srcLocal, const LocalTensor<uint8_t>& sharedTmpBuffer, const uint32_t dataSize) |
参数说明
参数名 |
描述 |
|---|---|
T |
操作数的数据类型。 |
highPrecision |
是否使能高精度接口,以提升运算准确度。 |
highPerformance |
是否使能高性能接口,以提升运算效率,注意:同时开启高精度和高性能模式相比于仅开启高性能模式可能会有性能下降。 |
参数名 |
输入/输出 |
描述 |
|---|---|---|
dstLocal |
输出 |
目的操作数。 类型为LocalTensor,支持的TPosition为VECIN/VECCALC/VECOUT。 Atlas A2训练系列产品/Atlas 800I A2推理产品,支持的数据类型为:half/float Atlas推理系列产品AI Core,支持的数据类型为:half/float |
srcLocal |
输入 |
源操作数。 类型为LocalTensor,支持的TPosition为VECIN/VECCALC/VECOUT。 源操作数的数据类型需要与目的操作数保持一致。 Atlas A2训练系列产品/Atlas 800I A2推理产品,支持的数据类型为:half/float Atlas推理系列产品AI Core,支持的数据类型为:half/float |
sharedTmpBuffer |
输入 |
临时空间。 类型为LocalTensor,支持的TPosition为VECIN/VECCALC/VECOUT。 该操作数的数据类型固定uint8_t。 用于接口内部复杂计算时存储中间变量,由开发者提供。 临时空间大小BufferSize的获取方式请参考GetGeluMaxMinTmpSize。 |
dataSize |
输入 |
实际计算数据元素个数,dataSize∈[0, min(srcLocal.GetSize(), dstLocal.GetSize())] |
返回值
无
支持的型号
Atlas A2训练系列产品/Atlas 800I A2推理产品
Atlas推理系列产品AI Core
约束说明
- 源操作数和目的操作数的Tensor空间可以复用。
- 操作数地址偏移对齐要求请参见通用约束。
- 仅支持输入shape为ND格式。
调用示例
#include "kernel_operator.h"
template <typename srcType>
class KernelGelu
{
public:
__aicore__ inline KernelGelu() {}
__aicore__ inline void Init(GM_ADDR src_gm, GM_ADDR dst_gm, uint32_t inputSize)
{
dataSize = inputSize;
src_global.SetGlobalBuffer(reinterpret_cast<__gm__ srcType *>(src_gm), dataSize);
dst_global.SetGlobalBuffer(reinterpret_cast<__gm__ srcType *>(dst_gm), dataSize);
pipe.InitBuffer(inQueueX, 1, dataSize * sizeof(srcType));
pipe.InitBuffer(outQueue, 1, dataSize * sizeof(srcType));
}
__aicore__ inline void Process()
{
CopyIn();
Compute();
CopyOut();
}
private:
__aicore__ inline void CopyIn()
{
AscendC::LocalTensor<srcType> srcLocal = inQueueX.AllocTensor<srcType>();
AscendC::DataCopy(srcLocal, src_global, dataSize);
inQueueX.EnQue(srcLocal);
}
__aicore__ inline void Compute()
{
AscendC::LocalTensor<srcType> dstLocal = outQueue.AllocTensor<srcType>();
AscendC::LocalTensor<srcType> srcLocal = inQueueX.DeQue<srcType>();
AscendC::Gelu(dstLocal, srcLocal, dataSize);
// AscendC::Gelu<srcType, true, false>(dstLocal, srcLocal, dataSize);
// AscendC::Gelu<srcType, false, true>(dstLocal, srcLocal, dataSize);
outQueue.EnQue<srcType>(dstLocal);
inQueueX.FreeTensor(srcLocal);
}
__aicore__ inline void CopyOut()
{
AscendC::LocalTensor<srcType> dstLocal = outQueue.DeQue<srcType>();
AscendC::DataCopy(dst_global, dstLocal, dataSize);
outQueue.FreeTensor(dstLocal);
}
private:
AscendC::GlobalTensor<srcType> src_global;
AscendC::GlobalTensor<srcType> dst_global;
AscendC::TPipe pipe;
AscendC::TQue<AscendC::QuePosition::VECIN, 1> inQueueX;
AscendC::TQue<AscendC::QuePosition::VECOUT, 1> outQueue;
uint32_t dataSize = 0;
};
template <typename dataType>
__aicore__ void kernel_Gelu_operator(GM_ADDR src_gm, GM_ADDR dst_gm, uint32_t dataSize)
{
KernelGelu<dataType> op;
op.Init(src_gm, dst_gm, dataSize);
op.Process();
}
输入数据(srcLocal): [-1.251 1.074 -6.137 -9.67 -5.066 -9.44 -3.588 -5.758 -7.484 -5.35 -9.62 -4.33 -6.66 -3.732 0.0841 -8.59 -6.3 -4.62 -3.059 -8.34 -8.24 -7.617 -7.93 -3.592 -3.268 -5.406 -9.49 5.633 -5.3 -9.36 -6.715 -5.727 ] 输出数据(dstLocal): [-0.1411 0.916 -0. -0. -0. -0. -0. -0. -0. -0. -0. -0. -0. -0. 0.0486 -0. -0. -0. -0. -0. -0. -0. -0. -0. -0. -0. -0. 5.633 -0. -0. -0. -0. ]