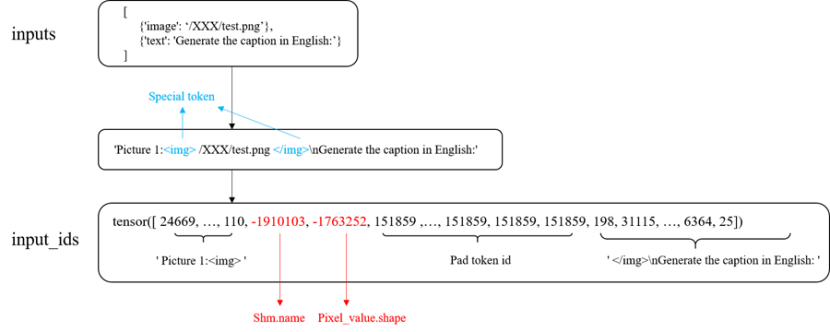
- tokenize() 函数输入
服务化传递过来的输入一定是List[Dict]类型的,其中字典包含的Keys目前有:image、video、audio、text四种。示例如下:
[ {"text": "What is in the image?"}, {"image": "/XXX/XXXX/image.png"}, {"video": "/XXX/XXXX/video.mp4"}, {"audio": "/XXX/XXXX/audio.mp3"} ] - tokenize() 函数实现
如上图所示,为输入的Promt信息和多媒体信息在tokenizer()函数中转换为Input Id的过程。
tokenizer()函数的实现分为以下步骤:
- 将输入转换为Str类型的query,并且用特殊的token作为分割,方便后续找到要填充的位置以及嵌入共享内存的name和数据的shape。
- 对转换后的query进行encode,得到token_ids。
- 遍历输入,加载并处理多媒体数据,计算input_ids的大小,进行padding。
- 将处理好的pixel_value数据存入共享内存,需要注意:
- 需要将数据转换为numpy.ndarray才能存入共享内存。
- dtype不做限制但是在后续读取数据时需要保持一致。
- 将共享内存的name和存入数据的shape进行编码,涉及到的编码函数已在如下公共代码中定义:
- 将编码好的name和shape嵌入input_ids中,返回一维的torch.Tensor(device=cpu)类型的input_ids。
代码示例如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42
def tokenize(self, inputs, **kwargs): # 1.转换 inputs 为 Str 的 query query = self.tokenizer.from_list_format(inputs) # 2. encode, qwen-vl 的这个函数是自己 padding 到固定长度,若模型是动态分辨率,请计算后在Padding input_ids = self.tokenizer([query], return_tensors="pt")["input_ids"].flatten() shm_name_save_path = kwargs.get('shm_name_save_path', None) shm_name_list = [] shape_value_list = [] image_type = "image" for single_input in inputs: if image_type not in single_input.keys(): continue # 3. 加载图片并预处理 image_pixel = _image_preprocess(single_input[image_type]) image_pixel = image_pixel[None, :] # ***************** Important Attention ********************************** # if shm_name_save_path is None: shm_name_save_dir = os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(single_input[image_type])) shm_name_save_path = os.path.join(shm_name_save_dir, "shm_name.txt") # ******************** Important Attention ******************************** # # 4. 存入共享内存 shm = create_shm(image_pixel.nbytes, shm_name_save_path) shared_array = np.ndarray(image_pixel.shape, dtype=np.float32, buffer=shm.buf) shared_array[:] = image_pixel # 5. 将共享内存的 name 编码为 int64, 将存入的Pixel value的shape编码为 int64 shm_name = encode_shm_name_to_int64(shm.name) shape_value = encode_shape_to_int64(image_pixel.shape) shm_name_list.append(shm_name) shape_value_list.append(shape_value) # 6. 将编码后的 name 嵌入 input_ids, 将编码后的 shape 嵌入 input_ids image_start_id = self.config.visual["image_start_id"] bos_pos = torch.where(torch.eq(input_ids, image_start_id))[0] image_num = bos_pos.shape[0] for i in range(image_num): input_ids[bos_pos[i] + 1] = shm_name_list[i] input_ids[bos_pos[i] + 2] = shape_value_list[i] return input_ids
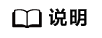
代码中标注了一段Important Attention代码,代码片段中的shm_name_save_path变量是用来存放共享内存地址的文件路径,以便在服务侧从该文件中读取共享内存地址释放共享内存。服务侧释放资源强依赖于传入的多媒体数据路径,因此服务化时该参数必须为“None”。
- forward() 多媒体数据处理
模型的flashcacusal类的forward()中,实际就是tokenize()的逆变换。
以Qwen-VL为例,forward()主要有以下操作步骤:
- 通过特殊的token找到多媒体数据的插入位置。
- 解码共享内存的name和数据的shape,从共享内存取出处理好的数据。需要注意get_data_from_shm()的第三个入参dtype是指存入共享内存时的类型,需要与存入时保持一致才能正确取出,这个函数返回tensor。
- 将上一步取出的shared_array送入处理多媒体数据的网络得到hidden features。
- 用hidden features替换掉input_ids中的pad tokens。
代码示例如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43
def forward( self, input_ids: torch.Tensor, ... ) -> torch.Tensor: if not self.ascend_weight: self.init_ascend_weight() self.init_kvcache(kv_cache) hidden_states = self.transformer.wte(input_ids) if is_prefill: if torch.any(torch.eq(input_ids, self.image_start_id)): # 1. 通过特殊的`token`找到多媒体数据的插入位置 bos_pos = torch.where(torch.eq(input_ids, self.image_start_id))[0] eos_pos = torch.where(torch.eq(input_ids, self.image_start_id + 1))[0] image_num = bos_pos.shape[0] images = [] pixel_array = [] for i in range(image_num): # 2. 解码共享内存的`name`和数据的`shape`,从共享内存取出处理好的数据 shm_value = input_ids[bos_pos[i] + 1] shape_value = input_ids[bos_pos[i] + 2] shared_array = get_data_from_shm(shm_value, shape_value, np.float32, self.device) pixel_array.append(shared_array) # 3. 送入ViT得到`hidden features` if len(pixel_array) != 0: pixel_array = torch.cat(pixel_array, dim=0) images = self.visual(pixel_array) else: images = self.visual.encode(images) # 4. 用`hidden features`替换掉`pad tokens` for i in range(image_num): hidden_states[bos_pos[i] + 1 : eos_pos[i]] = images[i] acl_inputs, acl_param = self.prepare_inputs_for_ascend( ... ) logits = self.execute_ascend_operator(acl_inputs, acl_param, is_prefill) return logits