功能说明
将输入tensor[m0, m1, ...mt, n](t大于等于0)的非尾轴长度相乘的结果看作m,则输入tensor的shape看作[m, n]。对输入tensor[m, n]按行做如下softmax计算:
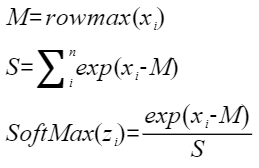
为方便理解,通过Python脚本实现的方式,表达其计算公式(以输入为ND格式为例)如下,其中src是源操作数(输入),dst、sum、max为目的操作数(输出)。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
def softmax(src): #基于last轴进行rowmax(按行取最大值)处理 max = np.max(src, axis=-1, keepdims=True) sub = src - max exp = np.exp(sub) #基于last轴进行rowsum(按行求和)处理 sum = np.sum(exp, axis=-1, keepdims=True) dst = exp / sum return dst, max, sum |
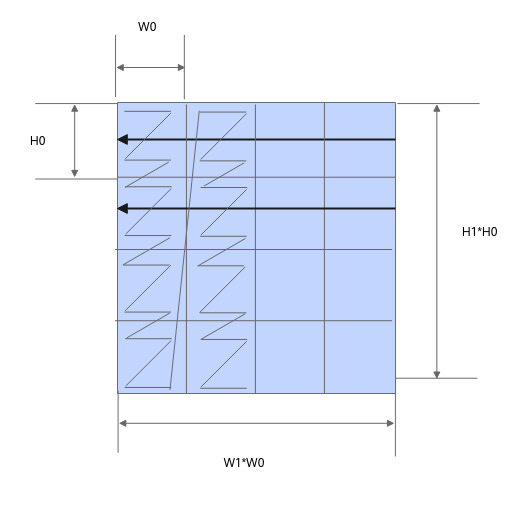
当输入的数据排布格式不同时,内部的reduce过程会有所不同:当输入为ND格式时,内部的reduce过程按last轴进行;当输入为NZ格式时,内部的reduce过程按照last轴和first轴进行,reduce过程如下图所示:
实现原理
以float类型,ND格式,shape为[m, k]的输入Tensor为例,描述SoftMax高阶API内部算法框图,如下图所示。
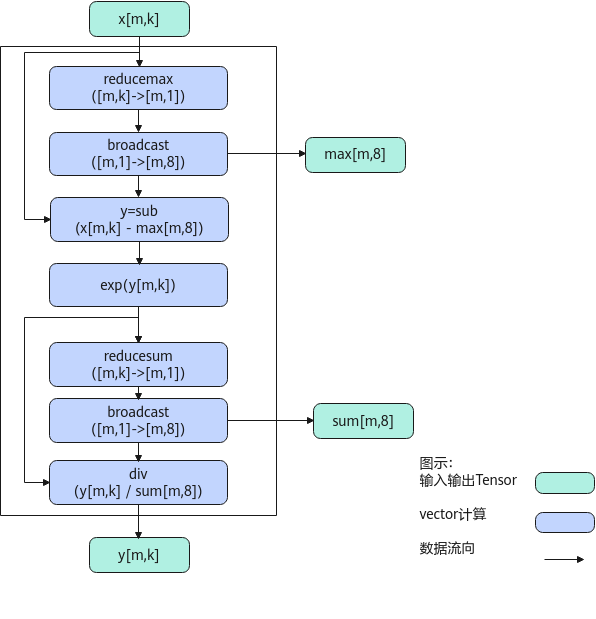
计算过程分为如下几步,均在Vector上进行:
- reducemax步骤:对输入x的每一行数据求最大值得到[m, 1]的结果,计算结果会保存到一个临时空间temp中;
- broadcast步骤:对temp中的数据([m, 1])做一个按datablock为单位的填充,比如float类型下,把[m, 1]扩展成[m, 8],同时输出max;
- sub步骤:对输入x的所有数据按行减去max;
- exp步骤:对sub之后的所有数据求exp;
- reducesum步骤:对exp后的结果的每一行数据求和得到[m, 1],计算结果会保存到临时空间temp中;
- broadcast步骤:对temp([m, 1])做一个按datablock为单位的填充,比如float类型下,把[m, 1]扩展成[m, 8],同时输出sum;
- div步骤:对exp后的结果的所有数据按行除以sum,得到最终结果。
函数原型
- 接口框架申请临时空间
- LocalTensor的数据类型相同
1 2
template <typename T, bool isReuseSource = false, bool isBasicBlock = false, bool isDataFormatNZ = false, const SoftmaxConfig& config = SOFTMAX_DEFAULT_CFG> __aicore__ inline void SoftMax(const LocalTensor<T>& dstTensor, const LocalTensor<T>& sumTensor, const LocalTensor<T>& maxTensor, const LocalTensor<T>& srcTensor, const SoftMaxTiling& tiling, const SoftMaxShapeInfo& softmaxShapeInfo = {})
- LocalTensor的数据类型不同
1 2
template <typename T, bool isReuseSource = false, bool isBasicBlock = false, bool isDataFormatNZ = false, const SoftmaxConfig& config = SOFTMAX_DEFAULT_CFG> __aicore__ inline void SoftMax(const LocalTensor<half>& dstTensor, const LocalTensor<float>& sumTensor, const LocalTensor<float>& maxTensor, const LocalTensor<half>& srcTensor, const SoftMaxTiling& tiling, const SoftMaxShapeInfo& softmaxShapeInfo = {})
- 不带sumTensor和maxTensor参数
1 2
template <typename T, bool isReuseSource = false, bool isBasicBlock = false, const SoftmaxConfig& config = SOFTMAX_DEFAULT_CFG> __aicore__ inline void SoftMax(const LocalTensor<T>& dstTensor, const LocalTensor<T>& srcTensor, const SoftMaxTiling& tiling, const SoftMaxShapeInfo& softmaxShapeInfo = {})
- LocalTensor的数据类型相同
- 通过sharedTmpBuffer入参传入临时空间
- LocalTensor的数据类型相同
1 2
template <typename T, bool isReuseSource = false, bool isBasicBlock = false, bool isDataFormatNZ = false, const SoftmaxConfig& config = SOFTMAX_DEFAULT_CFG> __aicore__ inline void SoftMax(const LocalTensor<T>& dstTensor, const LocalTensor<T>& sumTensor, const LocalTensor<T>& maxTensor, const LocalTensor<T>& srcTensor, const LocalTensor<uint8_t>& sharedTmpBuffer, const SoftMaxTiling& tiling, const SoftMaxShapeInfo& softmaxShapeInfo = {})
- LocalTensor的数据类型不同
1 2
template <typename T, bool isReuseSource = false, bool isBasicBlock = false, bool isDataFormatNZ = false, const SoftmaxConfig& config = SOFTMAX_DEFAULT_CFG> __aicore__ inline void SoftMax(const LocalTensor<half>& dstTensor, const LocalTensor<float>& sumTensor, const LocalTensor<float>& maxTensor, const LocalTensor<half>& srcTensor, const LocalTensor<uint8_t>& sharedTmpBuffer, const SoftMaxTiling& tiling, const SoftMaxShapeInfo& softmaxShapeInfo = {})
- 不带sumTensor和maxTensor参数
1 2
template <typename T, bool isReuseSource = false, bool isBasicBlock = false, const SoftmaxConfig& config = SOFTMAX_DEFAULT_CFG> __aicore__ inline void SoftMax(const LocalTensor<T>& dstTensor, const LocalTensor<T>& srcTensor, const LocalTensor<uint8_t>& sharedTmpBuffer, const SoftMaxTiling& tiling, const SoftMaxShapeInfo& softmaxShapeInfo = {})
- LocalTensor的数据类型相同
由于该接口的内部实现中涉及复杂的计算,需要额外的临时空间来存储计算过程中的中间变量。临时空间支持接口框架申请和开发者通过sharedTmpBuffer入参传入两种方式。
- 接口框架申请临时空间,开发者无需申请,但是需要预留临时空间的大小。
- 通过sharedTmpBuffer入参传入,使用该tensor作为临时空间进行处理,接口框架不再申请。该方式开发者可以自行管理sharedTmpBuffer内存空间,并在接口调用完成后,复用该部分内存,内存不会反复申请释放,灵活性较高,内存利用率也较高。具体内存复用方式可参考算子与高阶API共享临时Buffer。
接口框架申请的方式,开发者需要预留临时空间;通过sharedTmpBuffer传入的情况,开发者需要为tensor申请空间。临时空间大小BufferSize的获取方式如下:通过SoftMax/SimpleSoftMax Tiling中提供的GetSoftMaxMaxTmpSize/GetSoftMaxMinTmpSize接口获取所需最大和最小临时空间大小,最小空间可以保证功能正确,最大空间用于提升性能。
参数说明
|
参数名 |
描述 |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
T |
操作数的数据类型。 |
||||
|
isReuseSource |
预留参数,暂未启用,为后续的功能扩展做保留,必须使用默认值false。 |
||||
|
isBasicBlock |
srcTensor和dstTensor的shape信息和Tiling切分策略满足基本块要求的情况下,可以使能该参数用于提升性能,默认不使能。是否满足基本块的要求,可以采用如下两种方式之一判断:
针对 |
||||
|
isDataFormatNZ |
当前输入输出的数据格式是否为NZ格式,默认数据格式为ND,即默认取值为false。 针对 |
||||
|
config |
结构体模板参数,此参数可选配,SoftmaxConfig类型,具体定义如下:
配置示例如下:
此参数一般用于配合kernel侧tiling计算的接口使用。 注意:设置了oriSrcM与oriSrcK后,模板参数isBasicBlock不生效,计算数据是否为基本块由API内部判断并处理。 针对 针对 |
|
参数名 |
输入/输出 |
描述 |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
dstTensor |
输出 |
目的操作数。 类型为LocalTensor,支持的TPosition为VECIN/VECCALC/VECOUT。 dst的shape和源操作数src一致。 |
||
|
sumTensor |
输出 |
目的操作数。 类型为LocalTensor,支持的TPosition为VECIN/VECCALC/VECOUT。 用于保存softmax计算过程中reducesum的结果。
|
||
|
maxTensor |
输出 |
目的操作数。 类型为LocalTensor,支持的TPosition为VECIN/VECCALC/VECOUT。 用于保存softmax计算过程中reducemax的结果。
|
||
|
srcTensor |
输入 |
源操作数。 类型为LocalTensor,支持的TPosition为VECIN/VECCALC/VECOUT。 last轴长度需要32Byte对齐。 |
||
|
sharedTmpBuffer |
输入 |
临时空间。 类型为LocalTensor,支持的TPosition为VECIN/VECCALC/VECOUT。 该操作数的数据类型固定uint8_t。 接口内部复杂计算时用于存储中间变量,由开发者提供。 临时空间大小BufferSize的获取方式请参考SoftMax/SimpleSoftMax Tiling。 |
||
|
tiling |
输入 |
softmax计算所需Tiling信息,Tiling信息的获取请参考SoftMax/SimpleSoftMax Tiling。 |
||
|
softmaxShapeInfo |
输入 |
src的shape信息。SoftMaxShapeInfo类型,具体定义如下:
需要注意,当输入输出的数据格式为NZ格式时,尾轴长度为reduce轴长度即图2中的W0*W1,非尾轴为H0*H1。 |
返回值
无
支持的型号
约束说明
- src和dst的Tensor空间可以复用。
- sumTensor和maxTensor为输出,并且last轴长度必须固定32Byte,非last轴大小需要和src以及dst保持一致。
- sumTensor和maxTensor的数据类型需要保持一致。
- 操作数地址偏移对齐要求请参见通用约束。
调用示例
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 |
#include "kernel_operator.h" // static constexpr AscendC::SoftmaxConfig static_config = {true, 320, 64}; shape常量化使用 template <typename T> class KernelSoftmax { public: __aicore__ inline KernelSoftmax() {} __aicore__ inline void Init(__gm__ uint8_t *srcGm, __gm__ uint8_t *dstGm, const SoftMaxTiling &tilingData) { elementNumPerBlk = 32 / sizeof(T); src1Global.SetGlobalBuffer((__gm__ T *)srcGm); dstGlobal.SetGlobalBuffer((__gm__ T *)dstGm); pipe.InitBuffer(inQueueSrc, 1, height * width * sizeof(T)); pipe.InitBuffer(maxQueue, 1, height * elementNumPerBlk * sizeof(T)); pipe.InitBuffer(sumQueue, 1, height * elementNumPerBlk * sizeof(T)); pipe.InitBuffer(outQueueDst, 1, height * width * sizeof(T)); tiling = tilingData; } __aicore__ inline void Process() { CopyIn(); Compute(); CopyOut(); } private: __aicore__ inline void CopyIn() { AscendC::LocalTensor<T> srcLocal = inQueueSrc.AllocTensor<T>(); AscendC::DataCopy(srcLocal, src1Global, height * width); inQueueSrc.EnQue(srcLocal); } __aicore__ inline void Compute() { AscendC::LocalTensor<T> srcLocal = inQueueSrc.DeQue<T>(); AscendC::LocalTensor<T> sumTempLocal = sumQueue.AllocTensor<T>(); AscendC::LocalTensor<T> maxTempLocal = maxQueue.AllocTensor<T>(); AscendC::LocalTensor<T> dstLocal = outQueueDst.AllocTensor<T>(); AscendC::SoftMaxShapeInfo srcShape = {height, width, height, width}; AscendC::SoftMax<T>(dstLocal, sumTempLocal, maxTempLocal, srcLocal, tiling, srcShape); // AscendC::SoftMax<T, false, false, false, static_config>(dstLocal, sumTempLocal, // maxTempLocal, srcLocal, tiling, srcShape); 使用SoftmaxConfig类型的参数static_config,传入模板参数将shape常量化 outQueueDst.EnQue<T>(dstLocal); maxQueue.FreeTensor(maxTempLocal); sumQueue.FreeTensor(sumTempLocal); inQueueSrc.FreeTensor(srcLocal); } __aicore__ inline void CopyOut() { AscendC::LocalTensor<T> dstLocal = outQueueDst.DeQue<T>(); AscendC::DataCopy(dstGlobal, dstLocal, height * width); outQueueDst.FreeTensor(dstLocal); } private: AscendC::TPipe pipe; AscendC::TQue<AscendC::QuePosition::VECIN, 1> inQueueSrc; AscendC::TQue<AscendC::QuePosition::VECIN, 1> maxQueue; AscendC::TQue<AscendC::QuePosition::VECIN, 1> sumQueue; AscendC::TQue<AscendC::QuePosition::VECOUT, 1> outQueueDst; AscendC::GlobalTensor<T> src1Global, dstGlobal; uint32_t elementNumPerBlk = 0; uint32_t width = 64; uint32_t height = 320; SoftMaxTiling tiling; }; extern "C" __global__ __aicore__ void softmax_kernel_half( __gm__ uint8_t *srcGm, __gm__ uint8_t *dstGm, __gm__ uint8_t *tiling) { GET_TILING_DATA(tilingData, tiling); KernelSoftmax<half> op; op.Init(srcGm, dstGm, tilingData.softmaxTilingData); op.Process(); } |