功能说明
实现按元素做幂运算功能,提供3类接口,处理逻辑分别为:
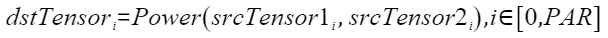
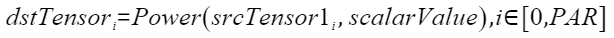
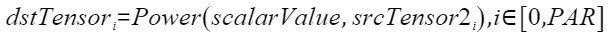
定义原型
- Power(dstTensor, srcTensor1, srcTensor2)
- 接口框架申请临时空间
template<typename T, bool isReplace = false, bool isBasicBlock = true>
__aicore__ inline void Power(const LocalTensor<T> &dstTensor, const LocalTensor<T> &srcTensor1, const LocalTensor<T> &srcTensor2);
- 通过tmpTensor入参传入临时空间
template<typename T, bool isReplace = false, bool isBasicBlock = true>
__aicore__ inline void Power(const LocalTensor<T> &dstTensor, const LocalTensor<T> &srcTensor1, const LocalTensor<T> &srcTensor2, const LocalTensor<T> &tmpTensor);
- 接口框架申请临时空间
- Power(dstTensor, srcTensor1, scalarValue)
- Power(dstTensor, scalarValue, srcTensor2)
- 接口框架申请临时空间
template<typename T, bool isReplace = false, bool isBasicBlock = true>
__aicore__ inline void Power(const LocalTensor<T> &dstTensor, const T& scalarValue, const LocalTensor<T> &srcTensor2, const LocalTensor<T> &tmpTensor);
- 通过tmpTensor入参传入临时空间
template<typename T, bool isReplace = false, bool isBasicBlock = true>
__aicore__ inline void Power(const LocalTensor<T> &dstTensor, const T& scalarValue, const LocalTensor<T> &srcTensor2);
- 接口框架申请临时空间
由于该接口的内部实现中涉及复杂的数学计算,需要额外的临时空间来存储计算过程中的中间变量。临时空间支持接口框架申请和开发者通过tmpTensor入参传入两种方式。
- 接口框架申请临时空间,开发者无需申请,但是需要预留临时空间的大小。
- 通过tmpTensor入参传入,使用该tensor作为临时空间进行处理,接口框架不再申请。该方式开发者可以自行管理tmpTensor内存空间,并在接口调用完成后,复用该部分内存,内存不会反复申请释放,灵活性较高,内存利用率也较高。
接口支持开启基本块功能,基本块计算是一种分块计算的方式。当输入的数据量较大,当前环境可提供的临时空间不充足时,可以开启基本块功能,分块进行计算。请根据如下公式判断是否需要开启基本块:
开发者当前环境可提供的临时空间大于n * InputSize * sizeof(datatype)时,可以不使用基本块,否则建议使用基本块。InputSize为输入元素个数,datatype为输入的数据类型。不同接口,不同数据类型对应n值如表1所示。
数据类型 |
Power(dstTensor, srcTensor1, srcTensor2) |
Power(dstTensor, srcTensor1, scalarValue) |
Power(dstTensor, scalarValue, srcTensor2) |
|---|---|---|---|
half类型 |
n = 12 |
n = 14 |
n = 14 |
float类型 |
n = 3 |
n = 4 |
n = 4 |
int32_t类型 |
n = 3 |
n = 4 |
n = 4 |
接口框架申请的方式,开发者需要预留临时空间;通过tmpTensor传入的情况,开发者需要为tensor申请空间。临时空间大小BufferSize的获取方式如下:
- 开启基本块功能,通过Power Tiling中提供的GetPowerMinTmpSize接口获取需要预留空间的大小。
- 不开启基本块功能,预留空间大小为 n * InputSize * sizeof(datatype),具体的n值如表1所示:以接口 Power(dstTensor, srcTensor1, srcTensor2)为例,对于half数据类型,BufferSize = 12 * InputSize * Sizeof(half);对于float数据类型,BufferSize = 3 * InputSize * Sizeof(float)。其中InputSize为输入元素个数。
参数说明
参数名 |
输入/输出 |
描述 |
|---|---|---|
dstTensor |
输出 |
目的操作数。 类型为LocalTensor,支持的TPosition为VECIN/VECCALC/VECOUT。 Atlas A2训练系列产品,支持的数据类型为:half/float/int32_t |
srcTensor1 |
输入 |
源操作数。 类型为LocalTensor,支持的TPosition为VECIN/VECCALC/VECOUT。 源操作数的数据类型需要与目的操作数保持一致。 Atlas A2训练系列产品,支持的数据类型为:half/float/int32_t |
srcTensor2 |
输入 |
源操作数。 类型为LocalTensor,支持的TPosition为VECIN/VECCALC/VECOUT。 源操作数的数据类型需要与目的操作数保持一致。 Atlas A2训练系列产品,支持的数据类型为:half/float/int32_t |
scalarValue |
输入 |
源操作数,类型为Scalar。源操作数的数据类型需要与目的操作数保持一致。 Atlas A2训练系列产品,支持的数据类型为:half/float/int32_t |
tmpTensor |
输入 |
临时内存空间。 类型为LocalTensor,支持的TPosition为VECIN/VECCALC/VECOUT。 数据类型需要与目的操作数保持一致。 Atlas A2训练系列产品,支持的数据类型为:half/float/int32_t 针对3个power接口,不同输入数据类型情况下,临时空间大小BufferSize的获取方式请参考定义原型。 |
isReuseSource |
输入 |
是否允许修改源操作数。该参数预留,传入默认值false即可。 |
isBasicBlock |
输入 |
是否使用基本块进行计算。 True: 若输入源数据数量大于基本块大小(1024),则会对输入数据进行分块,以块为单位进行处理。 False: 根据输入源数据量,分配相应的额外临时空间进行处理。 |
返回值
无
支持的型号
Atlas A2训练系列产品
约束说明
- 本指令函数由于只使用二级接口实现,运算量为目的LocalTensor的总长度。源操作数与目的操作数不允许同时使用(即地址不重叠)。
- 操作数地址偏移对齐要求请参见通用约束。
调用示例
本样例中只展示Compute流程中的部分代码。如果您需要运行样例代码,请将该代码段拷贝并替换样例模板中Compute函数的部分代码即可。
- Power(dstTensor, srcTensor1, srcTensor2)
Power<srcType, false, true>(dstLocal, srcLocal1, srcLocal2)
结果示例如下:输入数据(srcLocal1): [1.4608411 4.344736 ... 0.46437776] 输入数据(srcLocal2): [-5.4534287 4.5122147 ... -0.9344089] 输出数据(dstLocal): [0.12657544 756.1846 ... 2.0477564]
- Power(dstTensor, srcTensor1, scalarValue)
Power<srcType, false, true>(dstLocal, srcLocal1, scalarValue)
结果示例如下:输入数据(srcLocal1): [2.263972 2.902264 ... 0.40299487] 输入数据(scalarValue): 1.2260373 输出数据(dstLocal): [2.7232351 3.6926038 ... 0.32815763]
- Power(dstTensor, scalarValue, srcTensor2)
Power<srcType, false, true>(dstLocal, scalarValue, srcLocal2)
结果示例如下:输入数据(scalarValue): 4.382112 输入数据(srcLocal2): [5.504859 2.0677629 ... 1.053188] 输出数据(dstLocal): [3407.0386 21.225077 ... 4.7403817]
样例模板
#include "kernel_operator.h"
namespace AscendC {
template <typename srcType>
class KernelPower {
public:
__aicore__ inline KernelPower()
{}
__aicore__ inline void Init(GM_ADDR src1_gm, GM_ADDR src2_gm, GM_ADDR dst_gm, uint32_t srcSize)
{
src1_global.SetGlobalBuffer(reinterpret_cast<__gm__ srcType *>(src1_gm), srcSize);
src2_global.SetGlobalBuffer(reinterpret_cast<__gm__ srcType *>(src2_gm), srcSize);
dst_global.SetGlobalBuffer(reinterpret_cast<__gm__ srcType *>(dst_gm), srcSize);
pipe.InitBuffer(inQueueX1, 1, srcSize * sizeof(srcType));
pipe.InitBuffer(inQueueX2, 1, srcSize * sizeof(srcType));
pipe.InitBuffer(outQueue, 1, srcSize * sizeof(srcType));
bufferSize = srcSize;
}
__aicore__ inline void Process()
{
CopyIn();
Compute();
CopyOut();
}
private:
__aicore__ inline void CopyIn()
{
LocalTensor<srcType> srcLocal1 = inQueueX1.AllocTensor<srcType>();
DataCopy(srcLocal1, src1_global, bufferSize);
inQueueX1.EnQue(srcLocal1);
LocalTensor<srcType> srcLocal2 = inQueueX2.AllocTensor<srcType>();
DataCopy(srcLocal2, src2_global, bufferSize);
inQueueX2.EnQue(srcLocal2);
}
__aicore__ inline void Compute()
{
LocalTensor<srcType> dstLocal = outQueue.AllocTensor<srcType>();
LocalTensor<srcType> srcLocal1 = inQueueX1.DeQue<srcType>();
LocalTensor<srcType> srcLocal2 = inQueueX2.DeQue<srcType>();
LocalTensor<srcType> tmpLocal;
srcType scalarValue1 = srcLocal1.GetValue(0);
// srcType scalarValue2 = srcLocal2.GetValue(0);
Power<srcType, false, true>(dstLocal, scalarValue1, srcLocal2);
// Power<srcType, false, true>(dstLocal, srcLocal1, scalarValue2);
// Power<srcType, false, true>(dstLocal, srcLocal1, srcLocal2);
outQueue.EnQue<srcType>(dstLocal);
inQueueX1.FreeTensor(srcLocal1);
inQueueX2.FreeTensor(srcLocal2);
}
__aicore__ inline void CopyOut()
{
LocalTensor<srcType> dstLocal = outQueue.DeQue<srcType>();
DataCopy(dst_global, dstLocal, bufferSize);
outQueue.FreeTensor(dstLocal);
}
private:
GlobalTensor<srcType> src1_global;
GlobalTensor<srcType> src2_global;
GlobalTensor<srcType> dst_global;
TPipe pipe;
TQue<QuePosition::VECIN, 1> inQueueX1;
TQue<QuePosition::VECIN, 1> inQueueX2;
TQue<QuePosition::VECOUT, 1> outQueue;
uint32_t bufferSize = 0;
};
template <typename dataType>
__aicore__ void kernel_power_operator(GM_ADDR src1_gm, GM_ADDR src2_gm, GM_ADDR dst_gm, uint32_t srcSize)
{
KernelPower<dataType> op;
op.Init(src1_gm, src2_gm, dst_gm, srcSize);
op.Process();
}
} // namespace AscendC
extern "C" __global__ __aicore__ void kernel_power_operator(GM_ADDR src1_gm, GM_ADDR src2_gm, GM_ADDR dst_gm, uint32_t srcSize)
{
AscendC::kernel_power_operator<half>(src1_gm, src2_gm, dst_gm, srcSize); //传入类型和大小 }