该功能执行分析后通过Workload Analysis(比较工作点和屋顶的相对位置)输出分析结果。输出结果包括:
- Op list信息(列出所有工作在此区域的算子信息):
- 算子名
- 算子AI Core的时间占总AI Core时间的百分比(越大越有优化价值)
- 主要出现瓶颈的通道
- 距离当前的屋顶的百分比(比值越大表示越接近硬件上限瓶颈)
- 专家系统优化建议
输出结果如下:
图1 Roofline模型的算子信息列表及优化建议
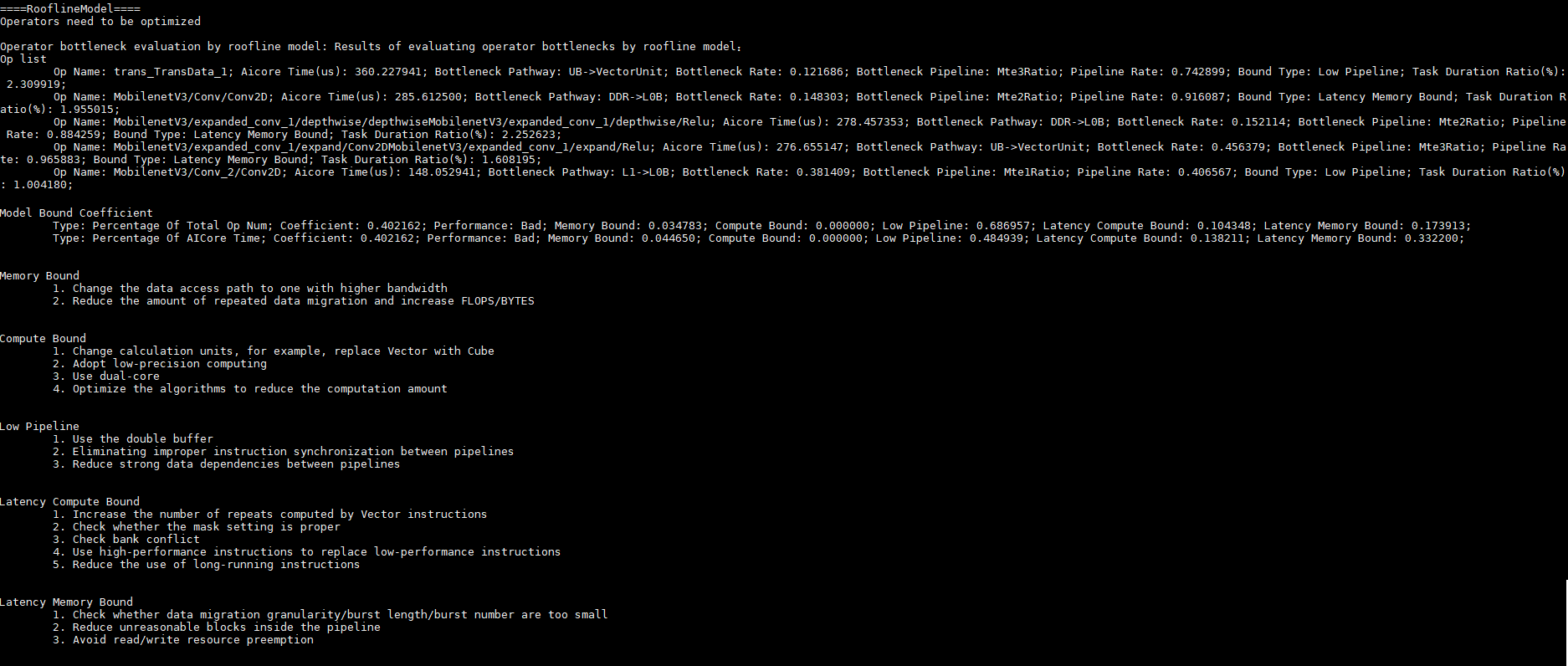

输出结果是将存在瓶颈算子的基本信息以列表形式输出,并提供优化建议,优化建议内容如下:
Memory Bound
内存瓶颈。
- Change the data access path to one with higher bandwidth
- Reduce the amount of repeated data migration and increase FLOPS/BYTES
Compute Bound
计算瓶颈。
- Change calculation units, for example, replace Vector with Cube
- Adopt low-precision computing
- Use dual-core
- Optimize the algorithms to reduce the computation amount
Low Pipeline
低流水利用率。
- Use the double buffer
- Reduce strong data dependencies between pipelines
- Eliminating improper instruction synchronization between pipelines
- Delete redundant pipe_barrier(PIPE_ALL).
Latency Compute Bound
潜在计算瓶颈。
- Increase the number of repeats computed by Vector instructions
- Check whether the mask setting is proper
- Check bank conflict
- Use high-performance instructions to replace low-performance instructions
- Reduce the use of long-running instructions
Latency Memory Bound
潜在内存瓶颈。
- Check whether data migration granularity/burst length/burst number are too small
- Reduce unreasonable blocks inside the pipeline
- Avoid read/write resource preemption
Model Bound Coefficient
模型瓶颈系数。
- Percentage Of Total Op Num:算子数量占比。
- Percentage Of AICore Time:AI Core耗时占比。
- Coefficent:瓶颈系数,所有算子的加权平均。
- Performance:性能优劣,取值为Good/Bad,瓶颈系数Coefficent大于0.8为Good,小于0.8为Bad。
- Memory Bound:内存瓶颈。
- Compute Bound:计算瓶颈。
- Low Pipeline:低流水利用率。
- Latency Compute Bound:潜在计算瓶颈。
- Latency Memory Bound:潜在内存瓶颈。
