功能简介
当用户网络中仅Batch的少量维度发生了变化,且维度变化的范围是有限的、可被枚举的,可以开启动态Shape图分档功能。通过将一张图划分为不同档位的方式,使一张图能支持多Batch,提升网络执行性能。
- 对于纯静态图,动态Shape分档功能允许输入Tensor的Shape在指定档位的维度上变化,而静态图的Shape不允许变化。
- 对于纯动态图,不分档的动态图中支持的Shape变化维度多于分档的动态图,而多出来的Shape变化范围很可能不是业务场景所需要的,因此动态图的执行性能会比分档后的动态图性能差。
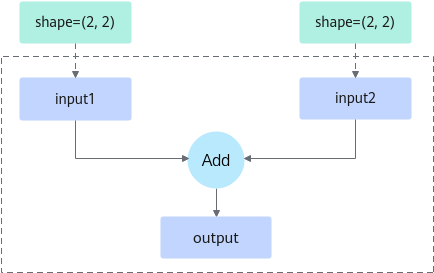
此处以图1为例,阐述三种图执行方式的差异。假设用户图只有Add算子,存在input1、input2、output三个tensor。编译该图时传入的input1与input2的shape都为(2, 2),而用户实际输入时input1与input2的shape有(2, 2)、(2, 2)与(4, 2)、(4, 2)两种。
- 静态图执行:
当torch.compile参数dynamic=False时,编译出的图仅支持shape为input1 (2, 2)、input2 (2, 2),此时执行性能最优,但支持的shape并不满足input1 为(4, 2)、input2为(4, 2)的场景。如果输入的shape为input1 (4, 2),input2 (4, 2),将会再次触发编译流程。
- 动态图执行:
当torch.compile参数dynamic=True时,编译出的图支持shape为input1 (-1, -1)、input2 (-1, -1) 此时图不仅支持input1与input2 shape为(2, 2)、(4, 2)两种场景,还支持(3, 3)、(4, 4)等任意input1与input2 shape相等的场景。由于动态图中算子的shape可变,无法一次将图中任务全部下发至Device计算,只能先下发一部分,返回计算结果后再下发另一部分,因此其执行性能比静态图差。
shape中的“-1”表示取值范围为1~正无穷。
- 动态shape图分档执行:torch.compile或torchair.inference.cache_compile编译出的图支持shape为input1 (-1, 2)、input2 (-1, 2) 。假设“-1”所在维度的档位设为[2, 2]、[4, 4],其中[]表示shape支持变化的范围。
- 档位1的[2, 2]:input1 shape为(2, 2), input2 shape为 (2, 2)
- 档位2的[4, 4]:input1 shape为 (4, 2), input2 shape为 (4, 2)
换言之整个分档图只支持这两种shape规格的输入。如果开启动态shape分档,会将每个档位的图转换为静态子图,能一次全部下发到Device侧, 因此执行性能优于动态图。

shape中的“-1”表示该维度支持被划分档位。
使用方法
- 通过set_dim_gears接口设置档位。以图1为例,设置过程如下:
import torch, torch_npu, torchair input1 = torch.ones(2, 2).npu() input2 = torch.ones(2, 2).npu() torchair.inference.set_dim_gears(input1, dim_gears={0:[2, 4]}) torchair.inference.set_dim_gears(input2, dim_gears={0:[2, 4]}) - (可选)设置动态分档的组合模式。
在设置config时通过dynamic_gears_merge_policy设置档位组合模式,默认为zip模式,也支持product模式,后者可以组合成更多的档位,用户按需选择合适的模式。
import torch_npu import torchair as tng config = tng.CompilerConfig() # 动态分档组合模式配置 config.inference_config.dynamic_gears_merge_policy = "zip" npu_backend = tng.get_npu_backend(compiler_config=config) ...
按1中配置,其档位组合结果如下:
- zip(默认模式):位置一一对应,input1、input2档位划分结果为[2, 2]、[4, 4],即input1、input2的shape支持(2, 2)、(2, 2)与(4, 2)、(4, 2)两种档位。
- product:排列组合,input1、input2档位划分结果为[2, 2]、[2, 4]、[4, 2]、[4, 4],即input1、input2的shape支持(2, 2)、(2, 2);(2, 2)、(4, 2);(4, 2)、(2, 2);(4, 2)、(4, 2)四种档位。其中input1、input2的shape为(2, 2)、(4, 2)与(4, 2)、(2, 2)两种档位在图1中并不符合相同shape相加的规则。

若采用zip模式配置档位繁琐时,可以使用product模式配置。
举个例子,当input3输入的shape为(2, 10),若想要对其划分6个档位(2, 10)、(3, 10)、(4, 10)、(2, 20)、(3, 20)、(4, 20),两种组合模式的配置代码如下:
- zip模式,档位配置复杂
torchair.inference.set_dim_gears(input3, dim_gears={0:[2, 3, 4, 2, 3, 4], 1:[10, 10, 10, 20, 20, 20]})
- product,档位配置简单
torchair.inference.set_dim_gears(input3, dim_gears={0:[2, 3, 4], 1:[10, 20]})
使用样例
import torch
import torch_npu
import torchair
from torchair.configs.compiler_config import CompilerConfig
class Model(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
def forward(self, x1, x2):
return x1 + x2
config = CompilerConfig()
# 默认zip模式,也支持设置product模式
# config.inference_config.dynamic_gears_merge_policy = "zip"
npu_backend = torchair.get_npu_backend(compiler_config=config)
model = Model().npu()
# 必须整图编译
model = torch.compile(model, fullgraph=True, backend=npu_backend)
npu_input0 = torch.ones([2, 2]).npu()
npu_input1 = torch.ones([2, 2]).npu()
# 设置档位
torchair.inference.set_dim_gears(npu_input0, {0: [2, 4]})
torchair.inference.set_dim_gears(npu_input1, {0: [2, 4]})
# 首次编译+执行,shape为(2,2)、(2,2)
print(model(npu_input0, npu_input1))
# 再次执行,shape为(4,2)、(4, 2)在档位中,不会触发重新编译
npu_input0 = torch.ones([4, 2]).npu()
npu_input1 = torch.ones([4, 2]).npu()
print(model(npu_input0, npu_input1))
开启TorchAir C++层日志,会显示图被划分的档位信息:
[INFO] TORCHAIR [concrete_graph/concrete_graph.cpp:123] Compiling concrete graph 0 with options: [INFO] TORCHAIR [concrete_graph/concrete_graph.cpp:125] ge.deterministic = 0 [INFO] TORCHAIR [concrete_graph/concrete_graph.cpp:125] ge.dynamicDims = 2,2;4,4 [INFO] TORCHAIR [concrete_graph/concrete_graph.cpp:125] ge.dynamicNodeType = 1 [INFO] TORCHAIR [concrete_graph/concrete_graph.cpp:125] ge.exec.atomicCleanPolicy = 1 [INFO] TORCHAIR [concrete_graph/concrete_graph.cpp:125] ge.exec.memoryOptimizationPolicy = MemoryPriority [INFO] TORCHAIR [concrete_graph/concrete_graph.cpp:125] ge.exec.outputReuseMemIndexes = 0 [INFO] TORCHAIR [concrete_graph/concrete_graph.cpp:125] ge.exec.reuseZeroCopyMemory = 1 [INFO] TORCHAIR [concrete_graph/concrete_graph.cpp:125] ge.featureBaseRefreshable = 0 [INFO] TORCHAIR [concrete_graph/concrete_graph.cpp:125] ge.inputShape = arg1_1:-1,2;arg2_1:-1,2 [INFO] TORCHAIR [concrete_graph/concrete_graph.cpp:125] ge.jit_compile = 2 [INFO] TORCHAIR [concrete_graph/concrete_graph.cpp:125] ge.topoSortingMode = 1
对应支持的档位如下,符合用户预期的档位。
- 档位1:npu_input0 shape=(2, 2),npu_input1 shape=(2, 2)。
- 档位2:npu_input0 shape=(4, 2),npu_input1 shape=(4, 2)。
接口说明
函数原型 |
def set_dim_gears(t: torch.Tensor, dim_gears: Dict[int, Union[List[int], Tuple[int]]) |
|
函数功能 |
设置图被划分的档位。 |
|
参数(IN) |
t |
必选参数,待分档的输入Tensor。 |
dim_gears |
必选参数,用于设置Tensor不同dim维度下的档位值。输入类型为Dict,其中key为dim维度(整型),value为档位值(整数列表或元组)。 说明:
|
|
参数(OUT) |
NA |
- |
返回值 |
NA |
|
使用约束 |
|
|