案例介绍
本案例呈现了在融合算子场景中,使用Matmul高阶API进行矩阵乘法计算时,A矩阵和B矩阵同时启用IBShare对性能的提升效果。
该案例的关键优化措施包括:
- 分核逻辑:以Cube核视角分核,Matmul计算结果输出到GM,提供给Vector核进行后续计算。
- 开启IBShare:A矩阵和B矩阵同时开启IBShare。
本案例的算子规格如下:
|
输入 |
Shape |
Data type |
Format |
|---|---|---|---|
|
x |
128,384 |
float16 |
ND |
|
y |
384,256 |
float16 |
ND |
开启IBShare和未开启IBShare的完整样例请参考matmulABshare样例和MatmulNoABshare样例。
获取性能数据
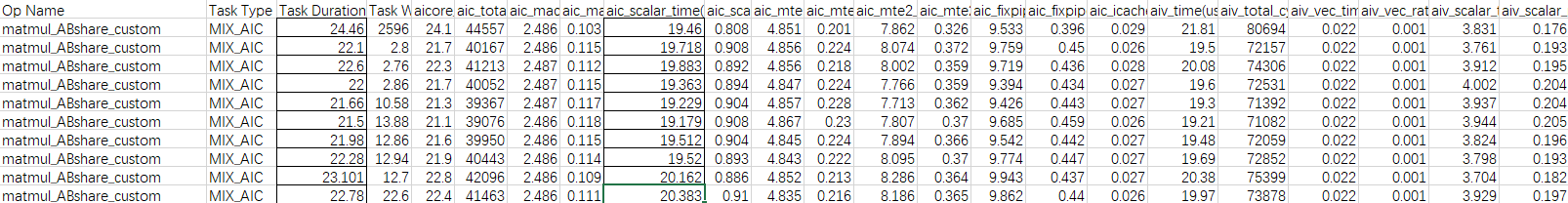
使用msProf工具获取算子的Profiling的数据,重点分析MTE2,Cube,Scalar的流水情况。
分析主要瓶颈点
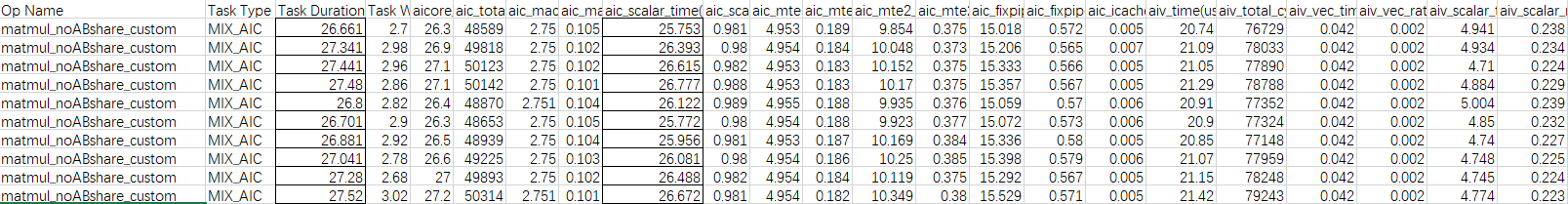
由以上Profiling数据,可以看出,算子执行多次的平均耗时为27.11us,aic_scalar_time的平均耗时为26.27us,当前性能瓶颈点为Cube的Scalar流水。
设计优化方案
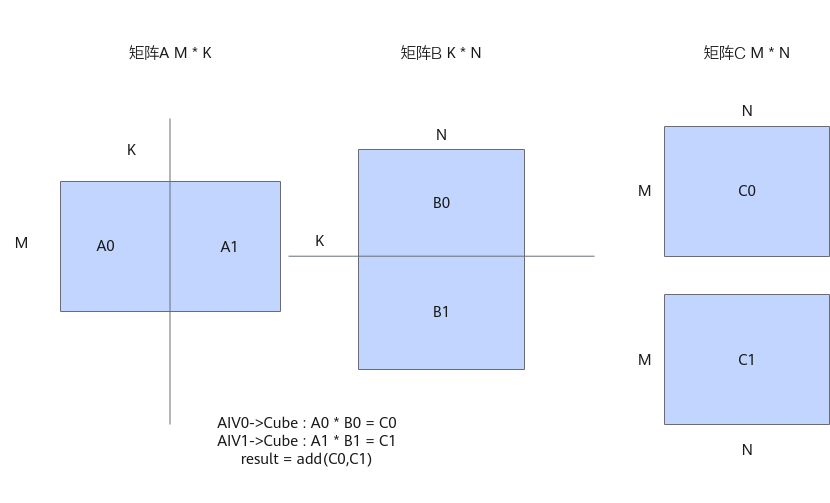
A矩阵和B矩阵均未开启IBShare时,数据需要根据K轴、M轴或N轴进行切分计算。这里以K轴切分为例,未开启IBShare之前,算子以AIV Block为视角进行tiling切分,AIV0发起A0*B0的计算,AIV1发起A1*B1的计算。
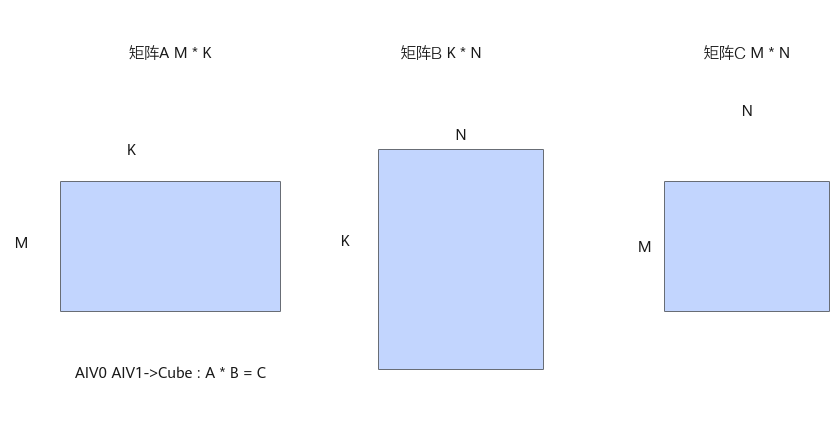
当A矩阵和B矩阵都启用IBShare时,可以一次性加载到L1 Buffer上,省去了切分,分开搬运的过程,同时Cube计算单元完全由AIV0单核驱动,发起一次计算,计算的结果由AIV0和AIV1共享,从而减少Cube响应的次数,减少Scalar计算。
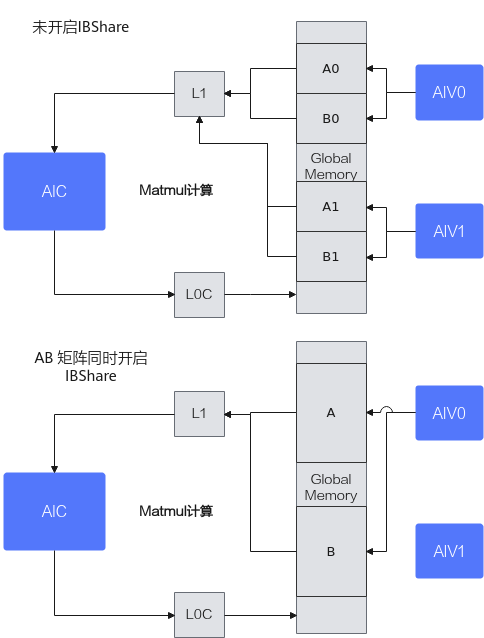
开启IBShare和不开启IBShare的数据交互对比示意图如下:
通过设置A和B矩阵MatmulType的IBShare均为true,开启该优化,具体代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 |
constexpr bool isABshare = true; template <typename aType, typename bType, typename cType> class MatmulABshareKernel { public: __aicore__ inline MatmulABshareKernel(){}; __aicore__ inline void Init(GM_ADDR a, GM_ADDR b, GM_ADDR c, GM_ADDR workspace, const TCubeTiling &tiling, AscendC::TPipe *pipe); __aicore__ inline void Process(AscendC::TPipe *pipe); __aicore__ inline void CalcOffset(int32_t blockIdx, const TCubeTiling &tiling, int32_t &offsetA, int32_t &offsetB, int32_t &offsetC); AscendC::Matmul<AscendC::MatmulType<AscendC::TPosition::GM, CubeFormat::ND, aType, false, LayoutMode::NONE, isABshare>, AscendC::MatmulType<AscendC::TPosition::GM, CubeFormat::ND, bType, false, LayoutMode::NONE, isABshare>, AscendC::MatmulType<AscendC::TPosition::VECIN, CubeFormat::ND, cType>> matmulObj; AscendC::GlobalTensor<aType> aGlobal; AscendC::GlobalTensor<bType> bGlobal; AscendC::GlobalTensor<cType> cGlobal; TCubeTiling tiling; }; template <typename aType, typename bType, typename cType> __aicore__ inline void MatmulABshareKernel<aType, bType, cType>::Init(GM_ADDR a, GM_ADDR b, GM_ADDR c, GM_ADDR workspace,const TCubeTiling &tiling, AscendC::TPipe *pipe) { this->tiling = tiling; aGlobal.SetGlobalBuffer(reinterpret_cast<__gm__ aType *>(a), tiling.M * tiling.Ka); bGlobal.SetGlobalBuffer(reinterpret_cast<__gm__ bType *>(b), tiling.Kb * tiling.N); cGlobal.SetGlobalBuffer(reinterpret_cast<__gm__ cType *>(c), tiling.M * tiling.N); int32_t offsetA, offsetB, offsetC; CalcOffset(AscendC::GetBlockIdx(), tiling, offsetA, offsetB, offsetC); // calculate offset aGlobal = aGlobal[offsetA]; bGlobal = bGlobal[offsetB]; cGlobal = cGlobal[offsetC]; } template <typename aType, typename bType, typename cType> __aicore__ inline void MatmulABshareKernel<aType, bType, cType>::CalcOffset(int32_t blockIdx, const TCubeTiling &tiling, int32_t &offsetA, int32_t &offsetB, int32_t &offsetC) { offsetA = 0; offsetB = 0; offsetC = 0; } |
验证优化方案性能收益
优化后执行多次的平均耗时:22.44us,较优化前有较大提升。
总结
融合算子场景下,Matmul A矩阵和B矩阵同时开启IBShare,以Cube核视角分核,可以有效减少Cube侧的Scalar开销,提升性能。