【优先级】中
【描述】对于Matmul得到的结果矩阵C(m, n),若后续需要和GM上的矩阵D(m, n)进行Add操作,则可以在GetTensorC接口或者IterateAll接口的GM通路上,将enAtomic参数设为1,开启AtomicAdd累加操作,在搬出矩阵C到GM时,矩阵C的结果将直接累加到矩阵D的GM地址上,从而实现与矩阵D的Add操作。
【反例】
将Matmul的结果矩阵C和GM上的矩阵D分别搬到UB上,做完Add操作后,结果再搬出到GM。这样至少要多分配一块UB内存给矩阵D,假设在分离架构的处理器上执行,将多做三次搬运操作(矩阵C从GM搬到UB、矩阵D从GM搬到UB、Add结果从UB搬出到GM)。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 | template <class A_TYPE, class B_TYPE, class C_TYPE, class BIAS_TYPE> __aicore__ inline void MatMulKernel(...) { ... AscendC::Matmul<A_TYPE, B_TYPE, C_TYPE, BIAS_TYPE, CFG_MDL> mm; TPipe pipe; REGIST_MATMUL_OBJ(&pipe, GetSysWorkSpacePtr(), mm); mm.SetTensorA(gm_a); mm.SetTensorB(gm_b); mm.SetBias(gm_bias); mm.IterateAll(gm_c); DataCopy(local_c, gm_c, c_size); DataCopy(local_d, gm_d, d_size); event_t eventIdMTE2ToV = static_cast<event_t>(GetTPipePtr()->FetchEventID(HardEvent::MTE2_V)); SetFlag<HardEvent::MTE2_V>(eventIdMTE2ToV); WaitFlag<HardEvent::MTE2_V>(eventIdMTE2ToV); Add(local_d, local_d, local_c, d_size); DataCopy(gm_d, local_d, d_size); ... } extern "C" __global__ __aicore__ void example_kernel(...) { ... typedef AscendC::MatmulType<TPosition::GM, CubeFormat::ND, half> aType; typedef AscendC::MatmulType<TPosition::GM, CubeFormat::ND, half> bType; typedef AscendC::MatmulType<TPosition::GM, CubeFormat::ND, float> cType; typedef AscendC::MatmulType<TPosition::GM, CubeFormat::ND, float> biasType; MatMulKernel<aType, bType, cType, biasType>(...); ... } |
【正例】
计算Matmul结果时,调用IterateAll接口或者GetTensorC接口搬运到矩阵D的GM地址上,同时将接口中enAtomic参数设为1,搬出到GM时,Matmul结果矩阵C会累加到矩阵D上,从而得到两个矩阵Add后的结果。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 | template <class A_TYPE, class B_TYPE, class C_TYPE, class BIAS_TYPE> __aicore__ inline void MatMulKernel(...) { ... AscendC::Matmul<A_TYPE, B_TYPE, C_TYPE, BIAS_TYPE, CFG_MDL> mm; TPipe pipe; REGIST_MATMUL_OBJ(&pipe, GetSysWorkSpacePtr(), mm); mm.SetTensorA(gm_a); mm.SetTensorB(gm_b); mm.SetBias(gm_bias); mm.IterateAll(gm_d, 1); // IterateAll接口中的enAtomic设为1 // while (mm. Iterate ()) { // mm.GetTensorC(gm_d, 1); // GetTensorC接口中的enAtomic设为1 // } ... } extern "C" __global__ __aicore__ void example_kernel(...) { ... typedef AscendC::MatmulType<TPosition::GM, CubeFormat::ND, half> aType; typedef AscendC::MatmulType<TPosition::GM, CubeFormat::ND, half> bType; typedef AscendC::MatmulType<TPosition::GM, CubeFormat::ND, float> cType; typedef AscendC::MatmulType<TPosition::GM, CubeFormat::ND, float> biasType; MatMulKernel<aType, bType, cType, biasType>(...); ... } |
【性能对比】
图1 Matmul使能AtomicAdd选项前后性能对比
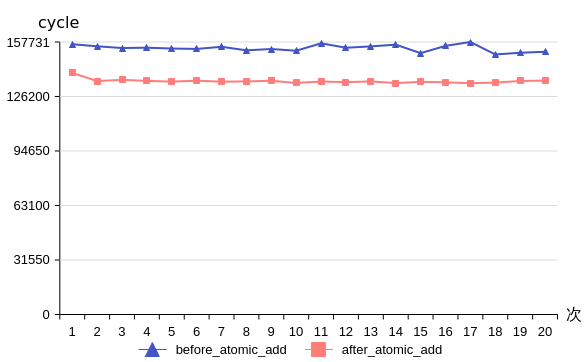

以矩阵维度M=64,N=256,K=256,矩阵D为(64, 256)为例,Matmul使能AtomicAdd选项前后的性能对比如上图所示,平均cycle数从开启AtomicAdd选项前的154181变为开启后的135054,性能优化12.4%。因此在这种场景下,使能AtomicAdd选项能获取更优的性能。